脳神経内科の名前は以前にくらべ浸透してきたと思いますが、それでもまだまだ精神科や心療内科と混同されておられる方も多いのではないでしょうか。「じゃあ脳神経内科ってどんな病気をみている科なのかな」と考えておられる皆さんの想像以上に、脳神経内科では多彩な病気をみています。例えば手足のしびれ、頭痛、筋力の低下といった症状から始まって、歩くとふらつく、呂律がまわらない、手がふるえる、単語がでてこない、物忘れ、まぶたが落ちてくる、目の焦点があわない、めまいがする、筋肉がこわばる、こむらがえりが頻発するといった症状の多くは神経系の病気です。うつや自律神経失調症といった心に関わる病気は精神科が担当です。
脳卒中、けいれん、髄膜炎・脳炎といった麻痺や意識障害をきたす病気は、緊急入院が必要な神経の病気です。意外かもしれませんが、脳神経内科は院内でも救急入院患者数が最も多い診療科の1つでもあります。さらに外来にはパーキンソン病や小脳変性症、筋萎縮性側索硬化症、筋無力症といった、いわゆる神経難病の患者さんが多数通院されています。これら難病の患者さんへ医療を中心とした数々の支援も私たちの大切な役目で、看護師や地域医療連携センター、地域の先生方と協力して行っています。
このように救急対応から慢性疾患のケアまで広い範囲をカバーしなくてはいけないので、脳神経内科の医師は、呼ばれればすぐ駆けつけるフットワークの軽さと同時に、身体的にも社会的にも複雑な状況を整理してゆく粘り強さが要求されます。医師それぞれの個性はありますが、診療科全体として急性疾患から慢性疾患までを万遍なくカバーできるように協力し合っています。
脳神経外科や救急部などと共に努力してきた脳梗塞急性期の血栓溶解療法や血管内治療も軌道に乗り、日本でも有数の脳卒中センターとなりました。また、血液疾患と関連するような神経症状の移植による治療、免疫異常による複雑な神経障害の治療にも積極的に取り組んできました。最近話題のパーキンソン病に対するiPS細胞を用いた治療も視野に入ってきました。現在も、これからもこういった新しい分野で、どこよりも高いレベルで患者さんのための正しい診療ができる脳神経内科であり続けることが私たちの目標です。
少しでも神経症状で困ったことがあったら、脳神経内科を受診してください。その場合、必ずかかりつけ医に紹介状を書いていただき、地域医療連携センターで予約をとっていただいてからの受診をお願いします。なお、当院ではある程度治療の方向が定まり、安定した患者さんは地域の先生に診ていただくようにしていますので、この点についてもご協力よろしく御願いいたします。
医師による的確な診断と治療、症状改善のためのリハビリスタッフとの協力。
急性疾患から慢性疾患まで、正確な診断と適切な治療を第一に、患者さんの生活背景を考慮しながら、スタッフ一丸となって医療に取り組んでいます。毎朝のカンファレンスにて診断・治療についてディスカッションを行い、適宜他科との連携も取りながら診療しています。

投薬や手術を行った上で、その後の患者さんの生活レベルを決定するのは継続的なリハビリテーションと言っても過言ではありません。多数のリハビリスタッフと密な連携を取り、患者さんの後遺症の軽減・回復に努めています。脳神経内科スタッフとリハビリスタッフの間で毎週カンファレンスを行い、協力して診療を行っています。

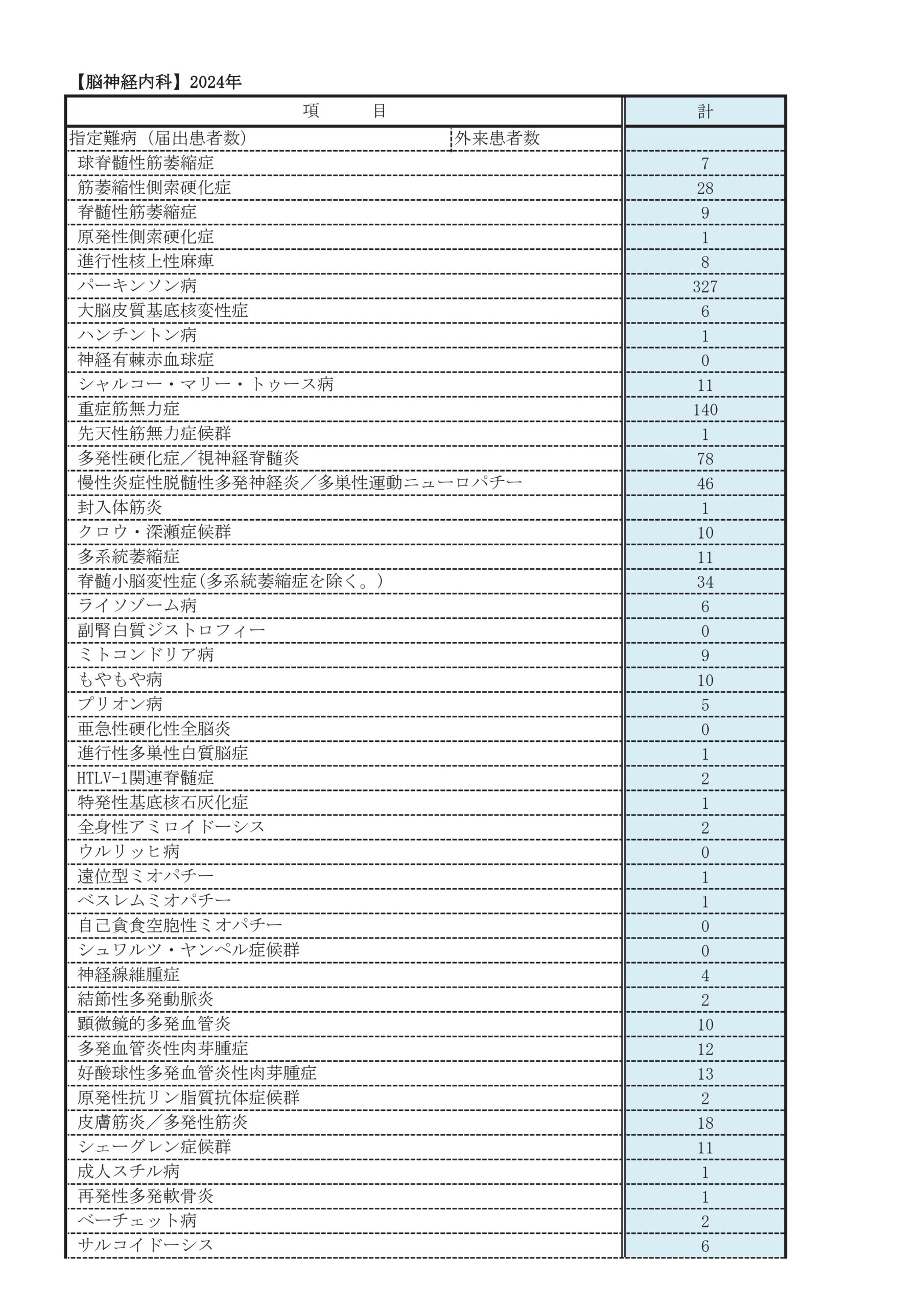
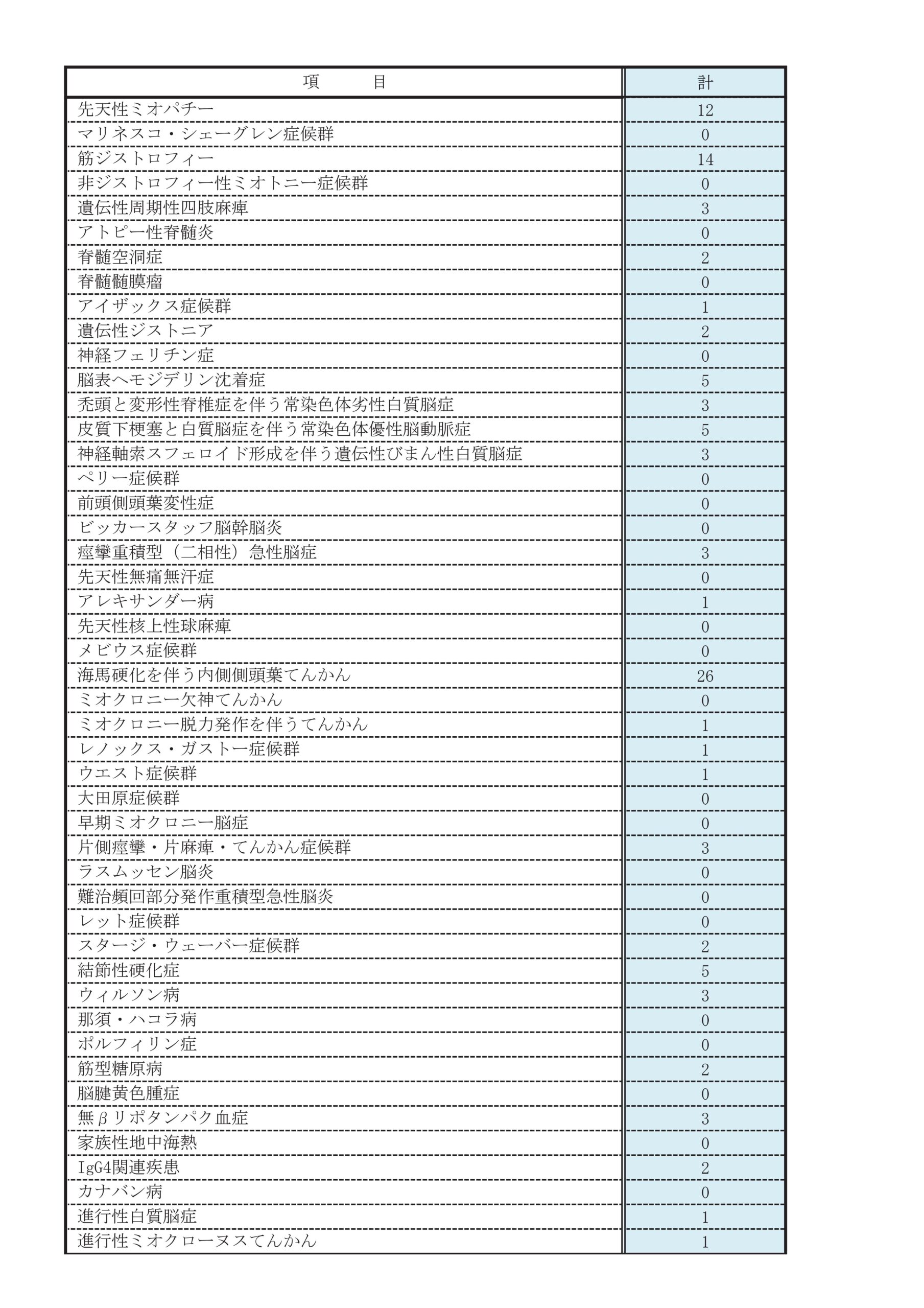
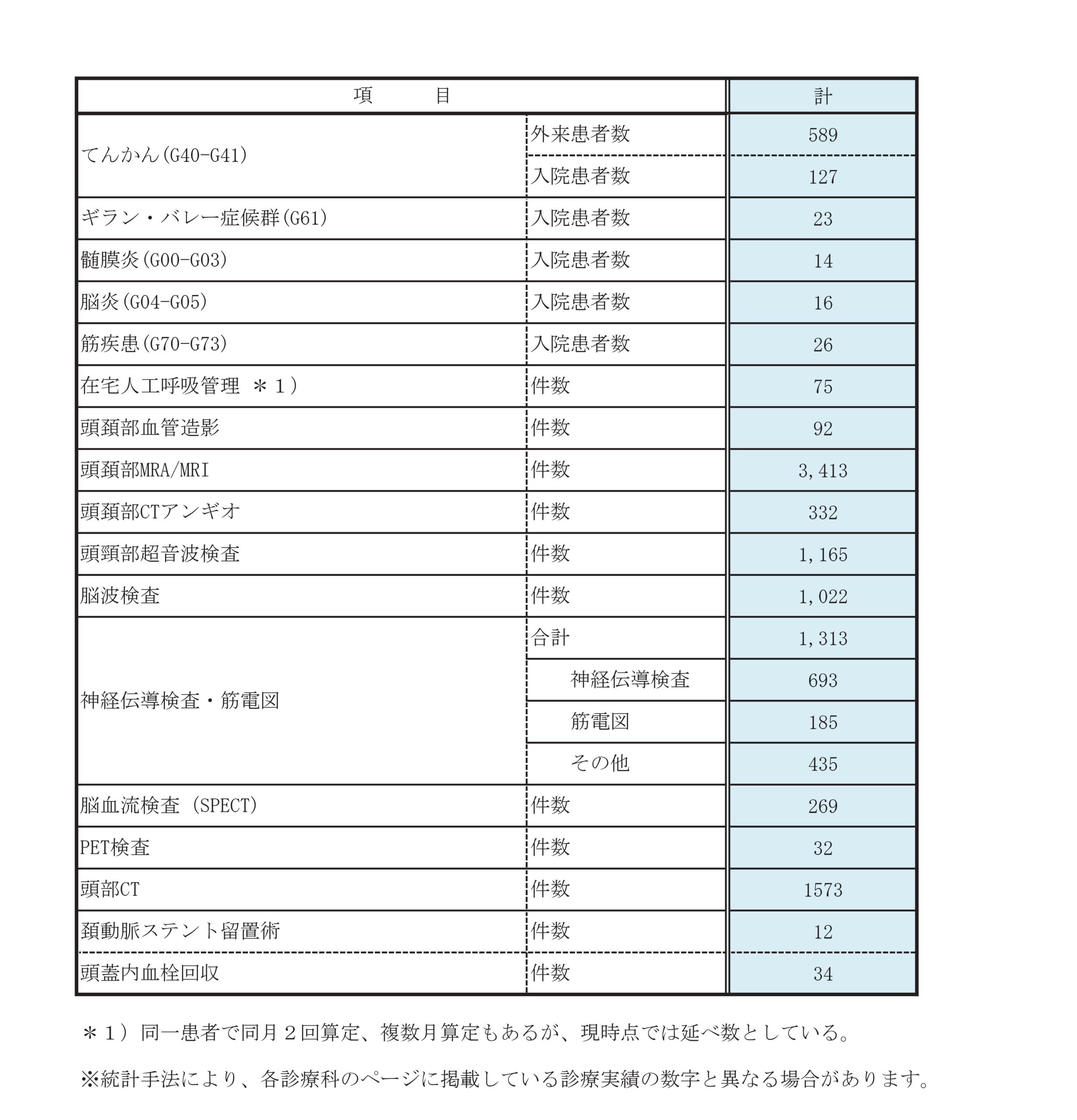
診療実績
主な疾患・治療法
脳卒中(脳梗塞・脳出血・頸動脈狭窄症)

脳の血管に血の塊(血栓)が詰まると「脳梗塞」、血管が破れると「脳出血」となります。頭部CTを撮像することにより、両者の判別は容易に可能です。脳梗塞には脳の血管が動脈硬化で細くなって詰まる場合と心臓などから血栓が飛んできて脳の血管に詰まる場合(脳塞栓)があります。また「頸動脈狭窄症」と言って、頸の動脈が細くなり、そこから血栓が飛んで脳梗塞を起こす場合もあります。当院では、総合脳卒中センターとして、脳外科と密に連携を取りながら、24時間365日受け入れ可能な体制を構築し、世界トップレベルの診療を目指しています。
脳梗塞
脳出血
原因として一番多いのが、高血圧です。入院後は、血圧を下げることによって出血の増悪を防ぎます。出血量が多く重篤な場合は、外科的に血腫除去を行うこともありますが、多くは保存的加療となります。非典型的な脳出血の場合は、脳血管奇形が原因の可能性もあることから、診断のために各種検査(頭部MRI・血管造影検査など)も積極的に行っています。
頸動脈狭窄症
頸動脈超音波検査・造影CT・MRI・カテーテルを用いた血管造影などの検査にて診断します。まずは内科的な治療が重要となりますが、内科治療抵抗性であったり、狭窄が重度であった場合、外科的治療が必要となります。「頸動脈内膜剥離術」と「頸動脈ステント留置術」がありますが、当科ではカテーテルを用いた血管内治療である「頸動脈ステント留置術」を積極的に行っており、ステントを用いて血管の細い部分を拡げます。術前には、脳血流を評価するための脳血流SPECT検査を行い、合併症のリスクを評価します。術後は、頸動脈超音波検査にて外来でのフォローアップを行います。
上記全てに共通しますが、発症後できるだけ早期に治療介入したほうが、受けられる治療の選択肢が多くなり、その後の後遺症も軽くすむ可能性が高くなります。突然の麻痺を自覚したり、家族や身近な方の突然の麻痺や呂律障害などの異常を発見した際は、迷わず早急に救急要請するようにお願いします。なお、急性期治療後はリハビリテーションが中心となるため、リハビリ専門の病院へ転院していただくことになりますので、御理解御協力のほどよろしくお願いいたします。
認知症の原因にはアルツハイマー型認知症が最多ですが、他にも様々な原因があります。臨床症状や画像検査(頭部MRIや核医学検査)、血液検査(甲状腺ホルモン、ビタミン欠乏など)などを用い、治療可能な認知機能障害を見極め、診断できた際は積極的に治療を行います。必要であれば、脳外科と連携の上、手術も検討します。アルツハイマー型認知症については、診断をつけた上で、地域連携において、かかりつけ医でのフォローアップをお願いしています。
症状
徐々に進行しますが、左または右手足のどちらかから始まり左右差が目立つことが多い疾患です。
診断
問診、身体診察に加えて下に述べるような各種検査、治療に対する反応性から総合的に診断をおこないます。
検査
- ダットスキャン:線条体におけるドパミントランスポーターの障害の程度を調べます
- MIBG心筋シンチグラフィー:パーキンソ病患者で高率にみられる心臓交感神経の障害の有無を調べます
- 頭部MRI:脳梗塞、正常圧水頭症などパーキンソン病と似た症状を起こす疾患を除外します
治療
ドパミン製剤を用いて体内に不足しているドパミンを補充することが基本ですが、これに加えてドパミン受容体作動薬(ドパミン受容体を直接刺激して活性化させます)やCOMT阻害薬、抗コリン剤など多くの薬物があり、症状に合わせてこれらを組み合わせて用います。また薬物療法で十分な改善が得られない場合に、手術により植込み装置を使って脳に直接電気刺激をおこなう方法もあります(DBS:視床下核深部脳刺激術)。また体のこわばりや姿勢の異常の進行を少しでも抑えるために、ストレッチを中心とした自分でできる体操も有用です。
症状
てんかん発作には、意識を失って手足をがくがくと震わせたり、突っ張ったりする、いわゆる痙攣発作以外にも、動作が停止して一点凝視し、無目的に口や手足を動かしてぼーっとする発作や、意識は失わずにみぞおちのあたりからこみ上げる感じを自覚したり、懐かしい感じがしたりする発作など極めて多彩なものがあります。高齢者ではてんかん発作の症状が非典型的となり、分かりにくくなることがあります。しかし、基本的にいずれの発作も、毎回同様の症状・経過をとるという特徴があります。
診断
てんかんの診断においては、まず始めに、発作性のエピソードがてんかん発作かどうかを判断することが最も重要となります。このため、発作症状を問診で詳しくお聞きします。患者さん自身は、発作中に意識を失っていることも多いため、目撃者と一緒に来院していただくか、目撃者にどのような発作であったかを具体的に聞いておいていただく必要があります。また、発作の様子を携帯電話などでビデオ撮影しておいていただけると、診断に非常に役立つことがあります。
これに加えて、必要に応じて以下のような脳波検査、CT・MRI検査などを行うことによって診断を確定します。
検査
脳波検査
大脳の神経細胞の電気活動を記録し、てんかん発作を生じうる異常な電気活動(てんかん性放電)などの有無を調べます。1回の検査で異常が認められない場合には、様々な賦活検査を加えて複数回検査を行うこともあります。
CT・MRI検査
脳の形態的異常の有無を調べ、てんかんの原因となる病変がないか確認します。
以上のような検査でも診断を確定できない場合や、外科的治療を検討する場合には、長時間ビデオ脳波モニタリング検査やSPECT・PET検査を行うこともあります。当院では長時間ビデオ脳波モニタリング検査は行っておりませんので、必要であれば専門施設へ紹介致します。
治療
抗てんかん薬を内服することで、てんかん発作を予防することが主な治療となります。てんかんの病型や年齢、性別、併存症などに応じて患者さんごとに最適な抗てんかん薬を選択します。抗てんかん薬には副作用もありますので、その有無に注意しながら使用します。抗てんかん薬を内服することによって、6〜7割の患者さんで全く発作が起こらなくなります。適切で十分量の抗てんかん薬2〜3種類を2年間以上使用しても発作が1年間以上抑制できずに日常生活に支障を生じる場合には、難治てんかんとして外科的治療の適応を検討します。外科的治療を考慮する場合には、専門施設へ紹介致します。
てんかんは年単位で付き合ってゆかねばならない病気ですので、自動車運転免許の取得・更新や就職、結婚、妊娠などのライフイベントごとに、患者さんと相談の上で治療を進めてゆきます。
ウイルス、細菌、真菌などが原因となり発熱、頭痛、意識障害、けいれんなどを引き起こします。診断には髄液検査が重要です。軽症から重症までさまざまな病態が含まれます。
普段はからだの中心で守られている中枢神経ですが, 何かを契機に微生物が侵入すると時に重篤な感染症に至ります。感染によって生じる炎症が脳に起こるものを脳炎といい、脳脊髄を包む髄膜に起こる場合を髄膜炎とよびますが、いずれも早期受診、速やかな治療開始が必要な病態です。原因微生物としてはウイルスと細菌が多いのですが、原虫や真菌なども原因になりえます。最近は検査の普及により、自己免疫機序によって生じる、自己免疫性脳炎も、しばしば診断されています。
症状
脳炎では発熱、意識障害、けいれんがあり、髄膜炎では頭痛や項部硬直(首の前後運動の抵抗)といった髄膜刺激徴候が有名ですが、これらを同時にきたすこともあります。時間単位、日単位に急激に増悪する頭痛や発熱が出現する場合には早めに受診してください。とくに意識がおかしくなってきた場合には緊急に処置が必要なこともありますので24時間いつでも救急外来へお越しください。
診断
診断のため、また原因微生物を同定して治療方針を決めるために髄液検査が必須です。髄液は局所麻酔をした腰部から細い針を刺して採取します。また血液検査、頭部CTやMRIも症例によって追加します。
治療
細菌感染症やヘルペスなど一部のウイルス感染症は、早期治療で炎症を落ち着かせないと、命にかかわる状態に至ることが多く、また回復しても重篤な後遺症を残す可能性があります。また、自己免疫性脳炎など特殊な疾患は、神経専門医の診察が必要です。中枢神経にダメージが加わってしまう前に専門医による適切な治療を開始することが何より重要です。
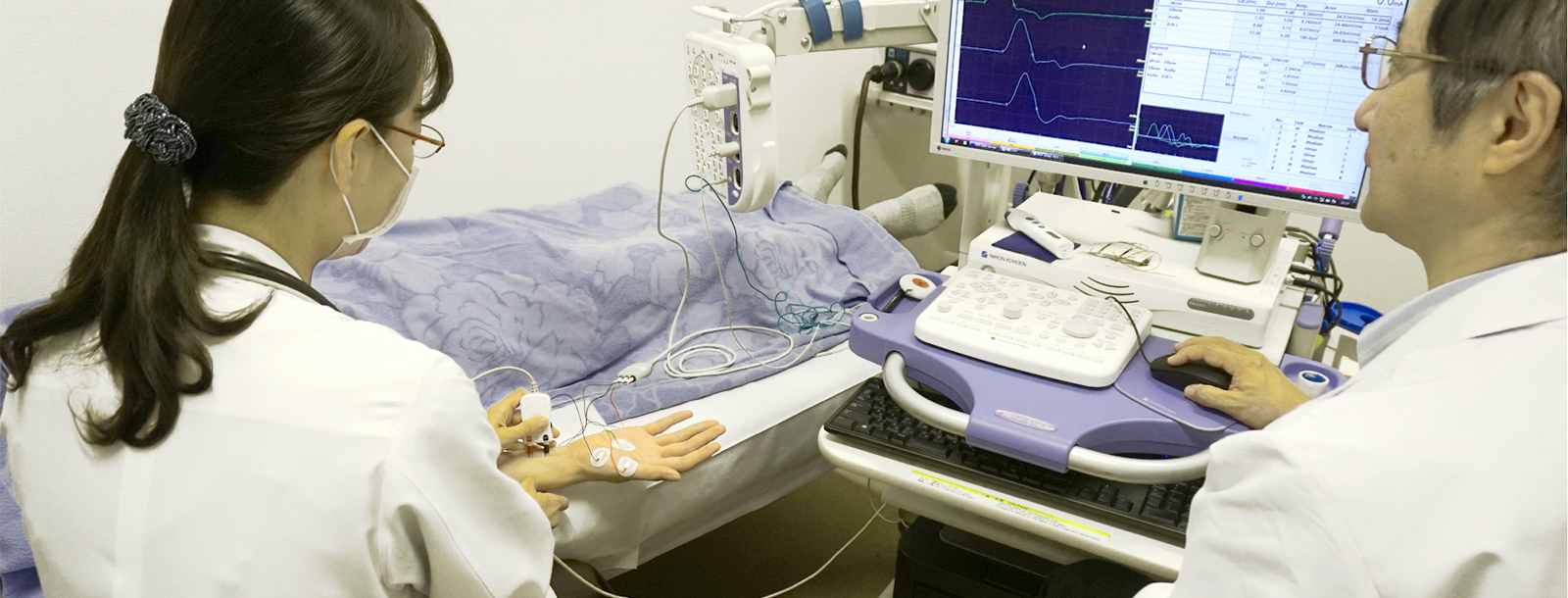
数日〜数ヶ月の経過で手足が動かしにくくなったという症状で来られた場合、末梢神経や、末梢神経と筋肉の接合部、筋肉が障害される病気が考えられます。どこが障害されているのか診断するには、血液検査などに加えて「神経伝導検査」や「針筋電図」がとても大切です。当院ではこれらの検査を積極的に行っており、緊急時にはいつでも検査できます。
ギランバレー症候群
数日の経過で手足がしびれたり力が入らなくなる病気で、末梢神経が障害されることによって症状が現れます。多くの例で、発症の1-2週間前に咳や痰などの風邪症状や下痢症状がみられます。リンパ球や抗体が誤って自分の末梢神経を攻撃してしまうことで発症する、自己免疫が関与した疾患です。神経伝導検査で診断をつけ神経障害の程度を調べることができます。無治療で自然回復する軽症例から、一時的にほとんど動けなくなる重症例まで様々です。重症の場合は後遺症として筋力低下が残ることもあるため、早期に診断し治療を開始することが大切です。治療としては、免疫グロブリン点滴療法や血液浄化療法があります。多くの場合、治療開始から1-2週間以内に症状がピークとなり、以後徐々に改善していきます。通常は一過性の病気ですが、まれに再発することもあります。
重症筋無力症
まぶたが下がったりや物が二重に見えるといったことで発症することが多いですが、飲み込みができない、言葉がしゃべれない、手足に力がはいらない、呼吸がしにくい、などの症状もみられます。持続的な運動が困難で、休息により脱力が回復するのが特徴です。運動神経の末端と筋肉が接合する部分の伝達がうまくいかないことにより発症する自己免疫性疾患です。上方視を続けると眼瞼下垂が悪化することや、握力を連続して測定すると回数を重ねるにつれ著しく握力が低下することなどでこの疾患を疑います。血液検査で疾患特異的な自己抗体の有無を調べたり、テンシロン試験や筋電図(反復刺激試験など)で確定診断します。治療はステロイド薬や免疫抑制剤(タクロリムス等)、免疫グロブリン大量療法などがあり、重症例では血漿交換療法も行います。重症筋無力症と胸腺の関連も強く、胸腺摘出術が適応になることもあります。急性期治療により症状が落ち着いた後も、再燃を予防するためには継続的にステロイド薬や免疫抑制剤の内服が必要になります。
筋炎
筋肉に炎症が起こることで、力が入りにくくなる病気です。多発筋炎、皮膚筋炎、封入体筋炎、ウイルス感染に伴う筋炎など様々な種類があります。筋炎の種類により異なりますが、間質性肺炎や皮膚症状、関節痛など筋肉以外の症状も合併することがあります。自己抗体などが関与した免疫学的機序により炎症が引き起こされると考えられています。血液検査に加え、針筋電図や筋生検で病理組織を解析することで診断します。治療は主にステロイド薬を使用しますが、症状や合併症によりタクロリムスやシクロフォスファミドなどの免疫抑制剤も併用します。最近では、免疫グロブリン大量療法も使えるようになっています。急性期治療により症状が改善した後も、再燃予防のためには継続的にステロイド薬や免疫抑制剤の内服が必要になります。ある種の筋炎は悪性腫瘍と合併することもあるため、悪性腫瘍を検索し治療することも大切です。
筋萎縮性側索硬化症(ALS)は、運動神経の障害によって四肢・体幹の運動、発声、飲み込み、呼吸などに必要な筋力が徐々に低下していく疾患です。厚生労働省によって難病に指定されており、発症すると筋肉のやせやぴくつきが目立つようになります。診断には筋電図が重要です。まだ現在の医学では進行を止める治療法は見つかっておりませんが、早期発見のうえ、ベストな医療、介護を提供できるよう取り組みます。
臨床研究
当科では、国の定める指針に基づいて現在様々な臨床研究や治験を行っています。
以下の研究は、「人を対象とする医学系研究に関する倫理指針」に則って、ここでの情報公開に基づいて実施しています。
対象患者様におかれましては、研究の趣旨をご理解いただき、ご協力を賜りますよう、よろしくお願い申し上げます。研究への協力に関して異議がある場合や、その他ご質問がある場合は、下記までご連絡下さい。
連絡先
神戸市立医療センター中央市民病院 脳神経内科部長 川本未知
神戸市中央区港島南町2丁目1−1
TEL 078-302-4321(大代表)
| 研究課題名 | 当院責任者 | 説明文 |
| tPA投与急性期脳梗塞患者における推定体重の実体重との乖離の検討 | 前川 嵩太 | |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical feature of anti-myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein antibody-associated cerebral cortical encephalitis with cerebrospinal fluid anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antibody co-positivity (髄液抗 NMDA 受容体抗体陽性の抗 MOG 抗体陽性皮質性脳炎の臨床的特徴に関する検討) | 春名孝太郎 | |
| Autoimmune glial fibrillary acidic protein astrocytopathyにおけるSoluble Interleukin-2 receptor αの検討 (Soluble Interleukin-2 receptor α in the pathophysiology of Autoimmune Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein Astrocytopathy) |
春名孝太郎 | |
| 塞栓源不明脳塞栓症の治療アルゴリズム構築を目的とした調査研究(ALGO ESUS) | 尾原信行 | |
| 髄液抗神経表面抗体陽性自己免疫性脳炎に関連したバイオマーカーの検討に関する研究 | 春名孝太郎 | |
| 自己免疫性脳炎における抗神経表面抗体の診断および長期予後に関する多施設共同研究 | 春名孝太郎 | |
| iTEchoの頚動脈エコーへの応用についてのパイロット研究 | 前川 嵩太 | |
| 針筋電図検査による筋萎縮性側索硬化症(ALS)の診断および予後予測に関する研究 | 今村大智 | |
| 網膜中心動脈閉塞症に対する低用量アルテプラーゼ静注療法に関する多施設共同後ろ向き観察研究
|
尾原信行 | |
|
脳主幹動脈閉塞患者における早期・遅発てんかん発症因子および予後に関する多機関後方視的観察研究 (PROgnosis of POst-Stroke Epilepsy in patients with cerebral Large Vessel Occlusion; a Multicenter Observational Retrospective study, PROPOSE-LVO) |
吉村元 | |
|
抗アミロイド抗体疾患修飾薬投与下におけるアミロイド関連画像異常を予測するバイオマーカーの開発 |
川本未知 | |
| 脳卒中後てんかんと後遺症の脳画像レジストリ研究 | 川本未知 | |
| 当院における抗MOG抗体陽性皮質性脳炎の検討~抗NMDAR抗体共陽性例に着目して~ | 春名孝太郎 | |
| 時定数2秒での脳波記録(infraslow activity)を使用した、TFNE(transient focal neurological episode)病態解明 | 川本未知 | |
| 機械的脳血栓除去術を受けた患者における虚血コア容積と神経学的転帰不良との間の時間変化の関係 | 前川嵩太 | |
| 閉塞血管の断端性状が機械的血栓回収療法の治療成績へ及ぼす影響の検討 | 高杉純司 | |
| サトラリズマブを導入した視神経脊髄炎関連疾患における経口ステロイド減量の試み | 石井淳子 | |
| 急性期脳波の異常自動検出プログラムの開発 | 川本未知 | |
| 人工知能(AI)を用いた神経生理検査の自動判別とデータ取得 | 幸原伸夫 | |
| 脳主幹動脈閉塞症に対する緊急再開通治療における、発症前依存疾患指数と治療後転帰の関連:後ろ向きコホート研究 | 藤原悟 | |
| COVID-19関連脳症の高次機能障害と脳血流の関連 | 小泉直史 | |
| 嚥下障害を有する急性脳卒中患者に対する早期積極的栄養療法の有効性の検討 | 前川嵩太 | |
| ラクナ梗塞発症後48時間以内に増悪する患者の来院時MRI画像を用いたAIモデルの構築 | 前川嵩太 | |
| 電子的診療録の自動構造化を有した自然言語処理解析装置の研究開発 | 尾原信行 | |
| BAT2「脳卒中研究者新ネットワークを活用した脳・心血管疾患における抗血栓療法の実態と安全性の解明」 | 尾原信行 | |
| 発症時刻不明脳梗塞に対する静注血栓溶解療法の多施設共同観察研究(THAWS 2) | 尾原信行 | |
| 睡眠中発症もしくは発症時刻不明脳梗塞に対するアルテプラーゼ静注血栓溶解療法試験の個別データ統合解析 Evaluation of unknown Onset Stroke thrombolysis trials(EOS) | 尾原信行 |
以下の研究や治験は患者様から同意をいただいた上で実施しています。
| 研究科題名 | 当院責任者 | 説明文 |
| SCAN「腫瘍合併虚血性脳卒中の臨床的特徴に関する多施設共同前向き観察研究」 | 幸原伸夫 | |
|---|---|---|
| ATIS-NVAF「非弁膜症性心房細動とアテローム血栓症を合併する脳梗塞例の二次予防における最適な抗血栓療法に関する多施設共同ランダム化比較試験」 | 坂井信幸 | |
| NAVIGATE-ESUS | 坂井信幸 | |
| RESPECT ESUS | 坂井信幸 | |
| L-DOPA併用パーキンソン病患者を対象としたHP-3000の第Ⅲ相並行群間比較試験幸原伸夫 | 幸原伸夫 |
お知らせ
医師、医師を目指す方向け当科のご紹介
※本コンテンツは、医師の方を対象とし、当医療機関についての理解を深めていただけるよう作成しているものであり、一般の方を対象とする宣伝・広告等を目的としたものではありません。 はじめまして、神戸市立医療センター中央市民病院 脳神経内科部長の川本 未知(かわもと みち)と申します。
当科は地域の基幹病院として、脳卒中から神経難病まであらゆる疾患に24時間365日対応しております。脳神経内科専門医8名と専攻医8名を有し、急性期IVRを含む脳卒中診療やALS・パーキンソン病など変性疾患のほか、髄膜炎などの感染症、多発性硬化症や末梢神経障害などの神経免疫疾患、てんかん・頭痛などの機能性疾患まで神経に関わる幅広い領域において、各領域のエキスパートを揃えて診療しています。
本日は脳神経内科の新しい治療と当院での取り組みの一部をご紹介いたします。
川本 未知
脳神経内科 部長
新たな抗体医薬品による片頭痛治療の変貌
片頭痛の有病率は10%と高く、高度の頭痛や嘔気のため患者のQOLは大きく阻害されており、社会的損失も大きくなっています。
従来の片頭痛治療では、発作時のNSAIDsやトリプタン製剤とカルシウム拮抗薬や抗てんかん薬を用いた予防治療が行われてきましたが、十分な発作頻度/程度の軽減が得られない症例も多くありました。
そのような中で、2021年に入り、片頭痛の病態に関わるカルシトニン遺伝子関連ペプチド(CGRP)をターゲットとした抗体医薬品が承認・発売されました。
従来法での治療効果が乏しかった症例で効果を確認
GRPは末梢の一次知覚神経の終末および遠位端に存在するペプチドで、主に末梢の感覚神経節や腸管の神経系に分布しています。片頭痛では三叉神経末端が刺激されてそこからCGRPが分泌され、血管拡張を誘発して片頭痛が生じます。
ガルカネズマブ(エムガルティ)、フレネズマブ(アジョビ)は抗CGRP抗体製剤であり、エレヌマブ(アイモビーグ)は抗CGRP受容体抗体製剤です。いずれも4週に1回~12週に1回の皮下注射製剤であり、過去に2剤以上の予防薬で治療が奏功しなかった症例に対しても有意な症状改善効果が見られ、安全性も高いです。
著効例がある一方で頭痛頻度50%以下にならいない症例も半数程度みられますが、そのようなケースでも頭痛強度の軽減が期待され、既存の治療効果が乏しい症例において試みるべき予防治療です。自験例でも月に10回以上トリプタン製剤を使用していた症例がトリプタンを必要とする頭痛がなくなり、QOLが大いに改善したケースがあります。当科では最新の片頭痛治療から命に関わる頭痛の鑑別まで迅速で幅広い対応が可能であり、頭痛診療にお悩みの際はぜひご紹介をお願いいたします。
パーキンソン病進行期における最新のデバイス治療
~Device aided therapy~
パーキンソン病は発症から5-7年を経過すると、様々な内服治療にもかかわらず、症状の日内変動(wearing off、on-off)やドーパ誘発性ジスキネジアといった運動合併症が出現します。
これらの運動合併症を伴ったパーキンソン病に対しては機器を用いたデバイス治療(DAT)が選択肢となります。
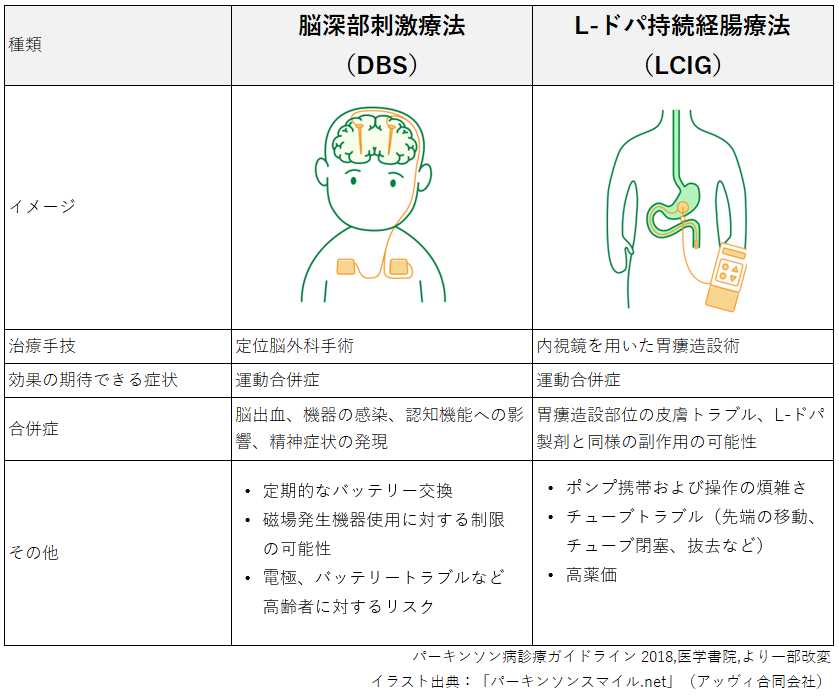
デバイス治療(DAT)の種類と特徴
現在本邦で承認されているものは深部脳神経刺激(deep brain stimulation: DBS)とレボドパ/カルビドパ配合経腸用液(levodopa continuous intestinal gel: LCIG)持続注入療法があり、最近ではMRガイド下集束超音波治療(FUS)が一部のパーキンソン病にも適応追加となりました。
DBSは刺激電極を視床下核や淡蒼球に留置、前胸部の皮下に刺激装置を埋め込みリードをつないで電気刺激を行うもので、LCIGは胃瘻を増設し専用のポンプとチューブで小腸内にレボドパを持続できに注入することで安定した血中濃度を維持する方法で、これらの治療は薬物療法でのコントロールが難しくなった患者に有効です。
当院では2003年よりDBS治療を開始しましたが、近年、デバイスの性能や手術時の位置決めに使用する画像処理技術は格段に進歩しており、症状変動に合わせた詳細な設定が可能な刺激装置を用いることでより安全で適切な治療が提供できるようになりました。
治療効果としてはoff時の底上げやレボドパ誘発制ジスキネジアの改善、offジストニアの改善、レボドパの減量などが期待できます。
紹介に迷われるケースであってもまずはご相談ください
DBSの適応は下記の項目が目安となります。
- レボドパへの反応が良好
- 明らかな認知症や重度の精神症状がない
- レボドパ5分割以上の内服でも日内変動やウェアリングオフが見られる
- ジスキネジアなど薬剤の副作用でさらなる増量が困難
- 75歳以下
DBSの適応外であっても、家族の援助を含め機器操作が可能な患者においてはLCIGを検討します。
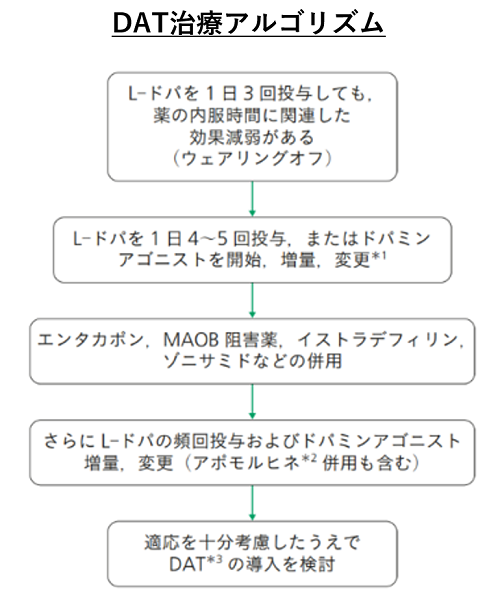
DAT治療アルゴリズムは下記の通りですが、当院ではこのような症例に1-2週間の入院精査を行い、DAT、LCIG等の治療方針を決定しています。
日常動作の多くに介助が必要な症例がDATにより介助がほぼ不要になるケースもあり、治療抵抗性の症例については、早めにDAT療法を検討することが重要ですので、適応に迷われるケースも含め気軽にご相談いただければ幸いです。
その他の抗体医薬品療法
近年、免疫の異常により引き起こされる神経疾患に対して、多くの抗体医薬品が用いられるようになりました。
疾患ごとに、いくつかご紹介いたします。
多発性硬化症(MS)に対するオファツムマブ
オファツムマブ(ケシンプタ)はCD20陽性B細胞を標的とする抗体医薬品で、月1回の皮下投与かつ簡便に使えるペン型デバイスであり、B細胞表面のCD20分子に結合し、強力なB細胞の溶解および減少を誘発します。多発性硬化症(MS)に適応となっており、標的選択性が高く、リンパ節でのB細胞減少と、脾臓でのB細胞温存を両立します。
MSは再燃と寛解を繰り返しながら次第に進行し、認知機能低下や身体障害など不可逆な症状を来すことが知られており、フィンゴリモド(イムセラ、ジレニア)やフマル酸ジメチル(テクフィデラ)など従来治療で再燃が抑制できない場合に考慮すべき治療です。
視神経脊髄炎(NMOSD)に対する最新の抗体医薬品
従来は視神経脊髄炎(NMOSD)の標準予防薬として、これまで経口ステロイドやアザチオプリンなどの免疫抑制薬などが使用されてきましたが、再発を抑制できない症例や、再発が抑えられてもステロイドの長期使用による副作用発現が大きな問題となってきました。
2019年、まず抗補体(C5)モノクローナル抗体製剤エクリズマブ(ソリリス)が、続いて抗IL-6レセプターモノクローナル抗体サトラリズマブ(エンスプリング)が認可され、いずれも極めて高い有効性を示し、ステロイドや免疫抑制剤の減量、中止が可能となりました。
2021年にはCD19に結合し、抗体を産生する形質芽細胞や形質細胞を含むB細胞を減少させる抗CD19モノクローナル抗体イネビリズマブ(ユプリズナ)が登場。本剤は投与間隔が6カ月に1回と患者への負担が少ないことが特徴です。
重症筋無力症に対する新たな治療選択
前述のエクリズマブ(ソリリス)が補体活性を阻止し神経筋接合部の伝達を改善することから適応となっており、ステロイドや免疫抑制剤でコントロール不良例や妊娠を希望する女性においての選択肢が広がっています。エクリズマブは補体の関与する多くの疾患への治療効果が期待されており、神経領域では現在ギランバレー症候群に対する治験も行われています。
早期の診断・治療が肝となる末梢神経障害
その他、四肢のしびれ痛みではじまり筋力低下を来す末梢神経障害においても、ANCA関連血管炎には抗CD20モノクローナル抗体リツキシマブ(リツキサン)が、好酸球性多発肉芽腫症(EGPA)には抗IL5モノクローナル抗体メポロリズマブ(ヌーカラ)が適応となり、虚血性視神経炎や脳梗塞で発症する巨細胞性動脈炎にも抗IL6レセプターモノクローナル抗体トシリズマブ(アクテムラ)が使用されます。
これらの疾患は数日単位で急速に進行することが多く、治療開始の遅れは後遺症の残存につながるためいくらよい治療法があっても早期診断早期治療ができなければ効果は期待できません。
当院の強みは、早期に診断するための診療体制や画像・電気生理診断が充実していることであり、受診当日や休日においても必要な検査を実施し、このような新規治療につなげることができます。
手足のしびれ痛み、筋力低下の背景にはこのような急ぎの治療を要する疾患が隠れていることがありますので、おかしいなと思われた場合は是非ご紹介いただければ幸いです。 また、エクリズマブなど使用開始にあたっては髄膜炎菌感染症予防にワクチン接種が必要ですが、当院では投与が望ましいとされるが国内にない髄膜炎菌B型ワクチン(Bexsero)も輸入常備しており、より安全性の高い治療を目指しています。
治療開始にあたって導入が必要な症例の紹介も受けており、遠慮なくご紹介いただきたいと思います。
脳卒中のことなら全ておまかせください!
(脳神経内科・脳卒中センター 尾原 信行)
当院の脳卒中センターは、2004年の開設当初から脳神経内科と脳神経外科が一体となって最先端の治療を提供する、国内随一の総合脳卒中センターです。
特に脳主幹動脈閉塞を伴う脳梗塞に対する機械的血栓回収療法では、救急隊と病院全体のチーム力を結集して、発症から最短時間で再開通を得るよう努めています。しかし私たちが力を入れているのは脳卒中の救急診療だけではありません。
脳卒中はまず発症しないこと、すなわち予防が最も大切です。脳や頚動脈の状態を調べ、生活習慣病や心房細動などのリスク因子に適切な介入を行うことは脳神経内科医の重要な役割です。
また、残念ながら脳卒中を発症してしまった時に、その原因を詳しく調べ、適切な再発予防につなげることも重要です。小さな脳梗塞をきっかけに全身の病気、たとえば「がん」や「感染症」、「血管炎などの自己免疫疾患」が見つかることもあり、たとえ症状は軽くても脳梗塞や脳出血が見つかれば、必ず私たちのような脳卒中センターへご紹介いただくことをお勧めします。
意外に思われるかもしれませんが、本邦ではこのような脳卒中の専門的診療をいまだに脳神経外科医のみが担っている地域も少なくありません。当院では脳神経内科と脳神経外科がそれぞれ専門的な役割を分担し、互いに協力することで質の高い脳卒中診療体制を維持しています。兵庫県内で脳卒中専門医、脳神経血管内治療専門医が在籍し、脳卒中の専門的診療を行うことができる脳神経内科は当院だけです。
脳卒中の予防から救急診療、そして慢性期治療までを、患者さん一人一人の併存疾患や社会背景に合わせ適切に管理していくことが私たち脳神経内科医の使命と考えています。
・脳血管、頸動脈狭窄の精査加療
・脳梗塞の塞栓源検索
・抗血栓薬の相談 など、脳卒中に関することでお困りの患者さんがいらっしゃいましたら、いつでも当科へご紹介ください。
先生方へのメッセージ
コロナ禍において、多くの診療機関において様々な診療制限が発生していると思われます。
当院も感染症指定病院としてコロナ診療に注力しておりますが、入院前PCR検査など考えられる最大の感染対策を行い、様々な工夫により通常診療を維持しております。今後も患者さん一人一人にとってあらゆる治療の可能性を検討し最善の医療が提供できるよう努めてまいりますので、お気軽にご相談いただければ幸いです。
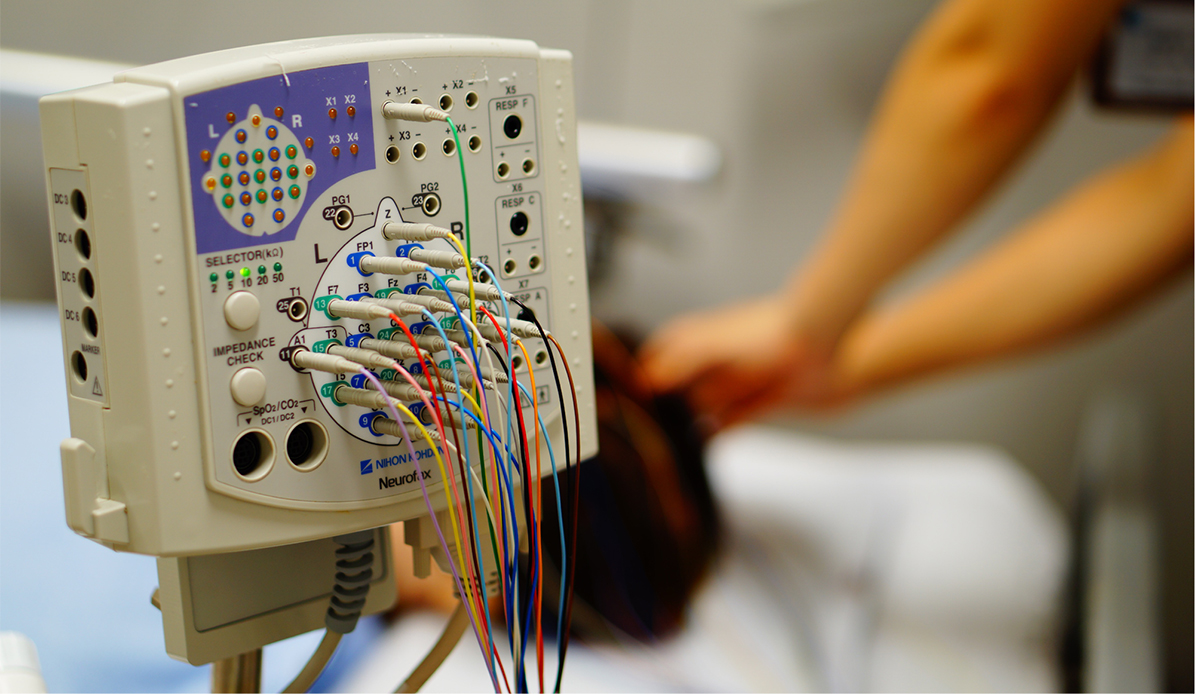
主な検査内容
医療設備として、CT(4台)、MRI(MRA)(2台)、脳血管撮影(DSA)、SPECT、EEG、EMG、 各種誘発電位、頸・頭蓋ドップラー検査、平衡機能検査などがそろっている。神経生理機能 検査室をセンターでは優秀な検査技師が医師と協力しながら検査を行っている。脳波、筋電図、 神経伝導検査、磁気刺激、各種脳誘発電位、頸部・頭蓋の超音波検査(エコー)を行っており、 いずれも日本のトップレベルの水準にある。