Lymphedema care outpatient guide
For patients suffering from lymphedema, under the direction of a doctor, we will explain about lymphedema, points to note about daily life, guidance on self-care methods (massage, bandage, skin care, exercise therapy), elastic clothing and We will introduce, select, measure, and explain how to use bandage products. We will help patients and their families with self-care so that they can deal with lymphedema well. We do not offer massages at our outpatient clinic. We teach our patients how to do their own massage.
* Depending on the patient's condition, we may ask you to receive care at another facility after consultation.
Guidance of medical examination
| Consultation day | Tuesday Thursday |
|---|---|
| place | A152 |
| time | 9:30~11:30 13:00~17:00 |
| medical treatment | Free medical treatment Complete reservation system Approximately 2 hours for the first visit and 1 hour for the follow-up visit |
| Target disease | Lymphoedema in venous and lymphatic disorders |
| Care content | Focus on self-care guidance based on Ferdi's compound physical therapy |
| responsible person | Rotating nurses qualified in lymphedema care |
How to make a reservation and notes
It is intended for outpatients of our hospital. Please consult your doctor and make an appointment for a lymphedema care outpatient clinic. Patients with foot lymphedema will be required to undergo an echocardiogram and a blood test (D-dimer: a value that indicates whether there is venous thrombosis activity) before the first visit. This test is covered by insurance.
What you need to know to live with lymphedema
Click each item for details
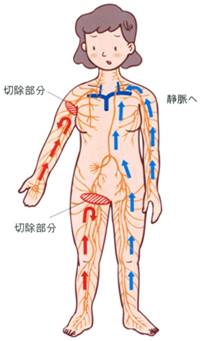
Lymphatic fluid, which carries unnecessary substances, proteins, fats, etc. in the cells of the body, is transported from every corner of the body using lymphatic vessels to a place called the venous angle under the neck and flows into the veins. After that, unnecessary substances are excreted from the body as urine through the kidneys. Just as food taken from the mouth is transported from the stomach to the intestines and excreted, lymphatic vessels also have the function of self-motility, and because they have anti-reflux valves, they always flow only toward the neck. However, if the function is impaired, such as when the lymphatic vessel is cut, the lymph fluid will accumulate without being transported from there. This condition is called lymphedema.
Sideways may form, but if there are no sideways, the accumulated lymph fluid will break the anti-reflux valve and flow back, causing swelling. Since lymphatic vessels are located in the subcutaneous tissue throughout the body, lymphatic fluid containing a large amount of protein and fat accumulates in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, causing lymphedema. Immediately after the onset of lymphedema, there is a lot of water (lymph fluid) in the subcutaneous tissue and it is soft, and the swelling is easy to improve if you rest. When the backflow of lymph reaches the surface of the skin, the skin becomes hard, and after a long period of time, fat and fibrous tissue increase, making it difficult to improve. Once lymphedema occurs, it is difficult to cure completely, but the condition can be controlled with proper care. Long-term lymphatic stagnation weakens the immune system, and small wounds, athlete's foot, and other bacterial infections and excessive burdens can cause cellulitis (I'll explain about Hokashikien later). easier.
What is compound physical therapy?
Conservative treatment for lymphedema. Based on a doctor 's diagnosis, it consists of four basic treatment methods: "skin care", "medical manual lymphatic drainage", "compression therapy", and "exercise therapy to promote drainage". In addition, we provide continuous support along with guidance on self-care and self-management at home. We make an individual treatment structure according to the degree of swelling and skin condition, and try to support the patient's continuous self-management method.
skin care
It is important to keep your skin clean and moisturised, and to keep your skin in good condition to prevent infections. Lymphatic stagnation leads to a weakened immune system, and if the skin is dry or damaged, bacterial infection can occur from there, making inflammation and cellulitis more likely to occur. Avoid sunburn in strong sunlight and be careful of burns or low-temperature burns such as hot carpets and warmers. If you have a swollen arm, use the non-swollen arm for blood sampling and injections. If unavoidable for treatment, consult a doctor or nurse. Bacterial infections, wounds, and skin symptoms such as athlete's foot and ingrown toenails are treated early. In addition, apply moisturizing cream to protect the skin, avoid being scratched by pets, avoid shaving with depilatories or razors, and apply cooling when there is redness or heat sensation. is required.
Medical manual lymphatic drainage (massage)
A soft massage is used to drain the lymph accumulated in the skin and skin tissue in the appropriate direction (healthy skin, lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, etc.). This reduces edema and improves the condition of hardened skin caused by lymphatic stasis.
compression therapy
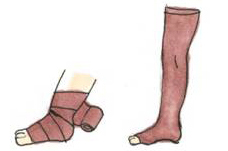
Exercise therapy under pressure
Cellulitis is an acute inflammation of the tissue under the skin. The onset of symptoms resembles those of a cold.
The main symptoms are
Chills: Chills, dullness, and shivering throughout the body.
Redness: The entire inflamed skin turns red, or a red rash appears.
Fever: A continuous sensation of heat locally. Fever of 38 degrees or higher.
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately and see a doctor. Temporarily stop massaging, pressing, and exercising other than moisturizing care and rest. Warm up with a blanket if you have chills. If you feel hot, let's cool down (evenly and firmly over a wide area). If inflammation occurs frequently, it is necessary to reconsider your daily life. Once the inflammation subsides, resume massage, compression, and exercise.
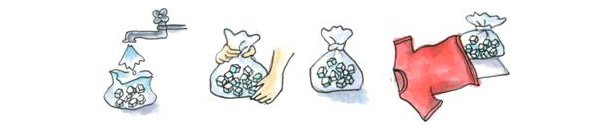
Cooling method (how to make an ice bag)
- Put two-thirds of tap water and about 20 household ice cubes into a plastic bag, remove the air, and secure the opening with a rubber band.
- Make a large ice bag by covering it with a soft cloth such as a T-shirt.
- Hold it in one place for about 30 seconds and roll it slowly to cool it down.
- If you don't feel hot even after 2 to 3 minutes after stopping the cooling, it's finished.
- Continue cooling until this heat is gone.
What is lymphorrhoea?
It means that lymph is pushed to the surface and becomes a small blister that breaks and leaks out. Change the clean gauze frequently so that the skin does not irritate. Apply a light pressure bandage.
- don't overdo it
- no burden
- does not hurt the skin
clothing
- For underwear and socks, choose soft materials such as loose cotton that won't constrict your skin.
- If your feet are swollen, choose shoes that are comfortable and easy to walk in.
food
- Try to maintain a normal weight.
- Keep alcohol in moderation.
- Refrain from smoking.
bedtime
- Sleep with your arms and legs slightly elevated with a soft cushion, etc., as much as you can comfortably.
- Take off elastic stockings when you go to bed at night.
work

Sports/Amusement
- Avoid excessive strain on your body by avoiding movements that stretch your arms or legs abruptly.
- Avoid long hot spring baths and sauna baths.
Travel/move
When you drive for a long time or travel by long-distance bus or airplane, move your body occasionally. Use compression therapy if possible.
Insurance coverage for compression garments
Due to the medical fee revision in 2008, up to 4 sets of compression garments (sleeves, stockings, etc.) purchased based on the doctor 's instructions can be applied for medical expenses twice a year (up to 2 sets per purchase). It is now accepted.
*There must be an interval of at least 6 months from the date of issuance of the previous receipt before the next application.
Disease eligible for payment
Malignant tumors with lymph node dissection (malignant melanoma, malignant tumors with lymph node dissection in the axilla including mammary glands, uterine malignant tumors, uterine adnexal malignant tumors, prostate malignant tumors and bladder, etc.) Lymphoedema of the extremities after surgery for pelvic malignancies of the urinary system (lymph node dissection)
Application procedure
Things to do before applying
- Go to the insurance association window to get an application form for payment of medical expenses, and fill in the necessary information.
- Ask them to create a "wearing instruction sheet for compression garments, etc."
- Those with a pressure indication of 30mmHg or more
- Compression of 20 mmHg or more is acceptable if there are special instructions from the doctor.
- Have a compression garment prescription, order, and payment "receipt" issued at an institution that handles compression garments.
application
Submit the following items to the insurance union window.
Documents required for application
- Application for payment of medical expenses
- Compression clothing, etc. Wearing instructions (some documents require a preparation fee)
- Receipt (dated after the date of issuance of the installation instructions)
- insurance card
- signature stamp
- Head of household account number
If you prepare 1 to 6 and submit it to the insurance union, you will receive a notification after 2 to 3 months of examination.
*In rare cases, the following may occur during combined physical therapy. Please consult your doctor before starting treatment if you have any of the following: Also, if you notice any changes in your physical condition since your first visit, or if you discover any new illnesses, be sure to let your therapist know.
Contraindications
- If you have acute inflammation due to infection [Inflammatory symptoms may be aggravated]
- Those with functional disorders such as the heart [The heart is overloaded and may cause pleural effusion, ascites, pericardial effusion, etc.]
- Those who may have venous disease (thrombophlebitis, venous thrombosis, etc.)
- Those who may have arteriosclerosis obliterans [Contraindications to compression: may cause aggravation of circulatory disturbance]
Notes
- Those with carotid sinus syndrome [Applying pressure to the carotid artery may cause fluctuations in blood pressure]
- Those with arrhythmia [Adding pressure to the carotid artery may put a strain on the heart]
- Persons with hyperthyroidism [Surgery on the neck may cause a sudden increase in thyroid hormone secretion and exacerbate symptoms.]
- Those with arteriosclerosis [Those with arteriosclerosis may cause vascular disorders]
- Those with renal dysfunction [Pleural effusion, ascites, etc. may occur due to changes in body fluid balance]
- Those with acute or chronic abdominal diseases (intestinal catarrh, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, etc.) [Applying strong pressure to the abdomen may induce inflammation, bleeding, or peritonitis]
- Patients with strong adhesions after intra-abdominal surgery or radiation therapy [By applying strong pressure to the abdomen, there is a risk of damaging the intestinal wall or bladder wall, which may lead to peritonitis]
- Those with an aortic aneurysm [The application of strong pressure to the abdomen may interfere with the aortic aneurysm]
- Those who have a history of intestinal obstruction [Applying strong pressure to the abdomen may induce peritonitis]
- Those who have a history of epilepsy [Applying strong pressure to the abdomen may cause epileptic seizures]
- Persons with sensory impairment in the affected limb [may not be aware of symptoms such as blood circulation disorders or pain]
- Those who may have hypersensitivity to textiles [contact dermatitis or eczema may occur]
- If a malignant tumor invades the lymphatic vessels and edema occurs, metastasis, recurrence, or worsening of the condition, etc. [First, consult with your doctor about the underlying disease, consider your general condition, and depending on the situation, stop the treatment. It is necessary to reconsider the continuation of lymphedema treatment and the content of treatment, such as
- In addition, liver disease, kidney disease, cardiovascular disease (hypertension, angina pectoris, arrhythmia, polycythemia, etc.), scleroderma, Zudek's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, infants, etc. [Consult with your doctor before receiving lymphedema treatment. There is a need]