神戸市の基幹病院また京都大学産婦人科の代表的な関連病院として、臨床経験豊富なスタッフが診療を行っています。 診療内容は、産科・周産期部門、婦人科・腫瘍部門の2つに分けられ、婦人科腫瘍の手術は悪性(癌)・良性ともに可能な限りなるべく低侵襲な内視鏡手術を行っています。24時間体制で 産婦人科救急にも対応しています。
産科・周産期部門
兵庫県で2番目の総合周産期センターとして、年間約800人の方が分娩されています。母体合併症の治療・管理に重点を置き、当院の専門各科と協力して妊娠・分娩中の援助と治療を行っており、母体合併症を適応とする硬膜外無痛分娩も行っております。胎児に異常がある場合は、胎児エコー・MRIなど最新の医療技術を用いて診断・救命に努めています。新生児科には新生児集中治療室(NICU)があり、未熟児や病気をもった赤ちゃんの総合的な治療を行っています。お母さんや赤ちゃんの状態が急に悪くなった時に、その命を救うためのシステムとしての超緊急帝王切開や、分娩時の大量出血に対する緊急処置や集中治療などを新生児科、麻酔科、救急救命科などと協力して行う体制を整えています。
婦人科・腫瘍部門
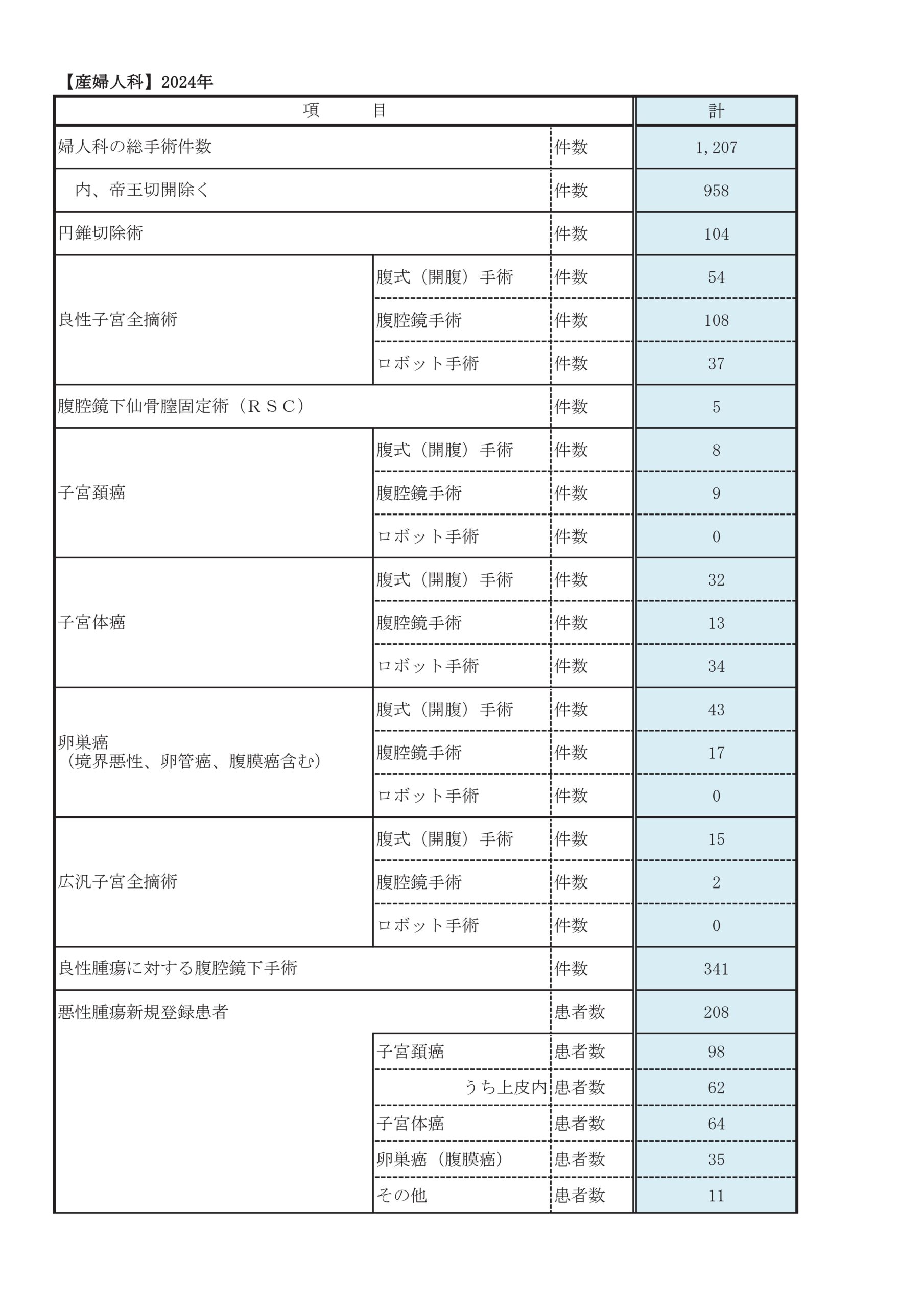
年間婦人科手術数は1000例以上あり、合併症などのため他病院で実施困難な患者さんの手術・治療も行っています。不妊の原因となる子宮内膜症や子宮筋腫に対する手術治療も多く実施しています。悪性の病気(癌や肉腫)は、がん拠点病院として、子宮頸癌・子宮体癌・子宮肉腫・卵巣癌など多くの患者さんの集学的治療をしています。早期癌には妊孕性温存手術・腹腔鏡手術・ロボット支援(ダヴィンチ)手術、進行癌へは神経温存手術・リンパ浮腫低減手術・ 術前化学療法・他科合同拡大手術・高度放射線治療など最新の治療を積極的に行っています。
内視鏡手術
年間腹腔鏡手術は450例以上で近畿有数です。子宮筋腫核出術・子宮摘出術・卵巣嚢腫摘出術・子宮外妊娠手術など多くの良性疾患で腹腔鏡手術が可能です。早期子宮体癌に対する腹腔鏡手術も以前から行っており、2020年までに250人以上の子宮体癌の患者さんの腹腔鏡手術を行っています。2018年4月からは、子宮体癌に対してロボット支援(ダヴィンチ)手術も導入しています。2015年からは先進医療、その後2018年4月から保険診療となった子宮頸癌に対する腹腔鏡手術も導入しています。2023年よりvNOTES(経腟的腹腔鏡手術)も導入しています。
当科では産科・婦人科・内視鏡手術、各分野の専門医を含むエキスパートによるチーム医療体制を整えています。
〈医局員〉

〈内視鏡手術〉
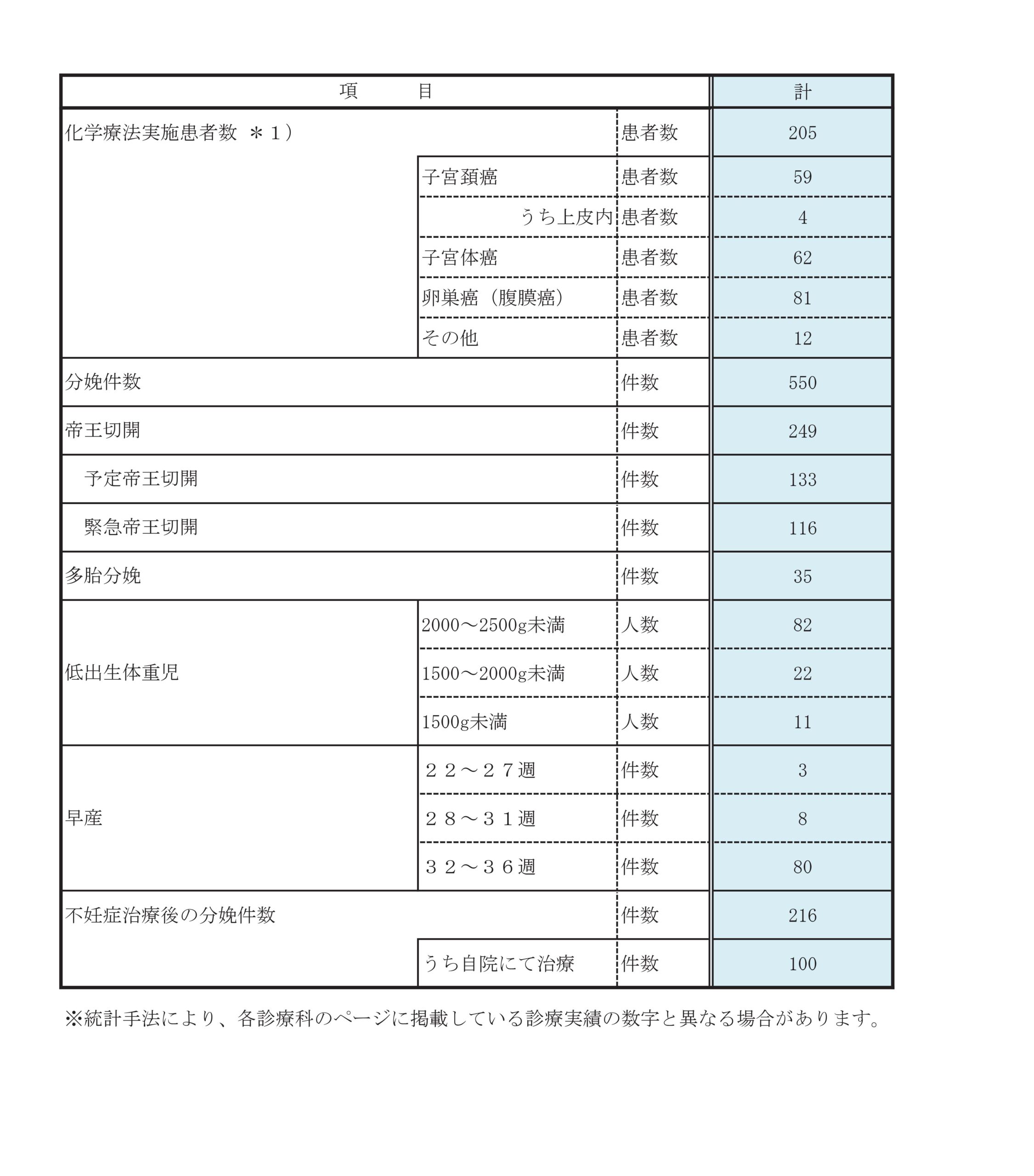
診療実績
全国有数のレベルの総合病院であることを生かして、専門各科と連携しつつ、腫瘍、周産期、 不妊、救急など産婦人科全般の高度医療を行っています。
診療科別統計
主な疾患・治療法
婦人科
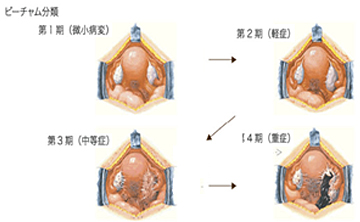
悪性腫瘍が疑われた場合、検査(内診、直腸診、超音波、CT/MRI、腫瘍マーカーなど)を行い、病期(ステージ)を推定し、治療法を選択します。癌の治療は、手術・放射線・化学療法があります。
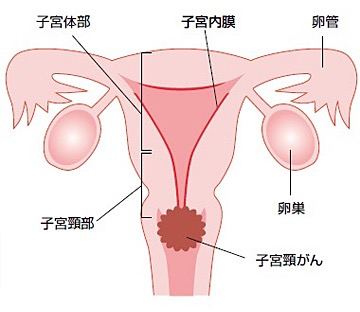
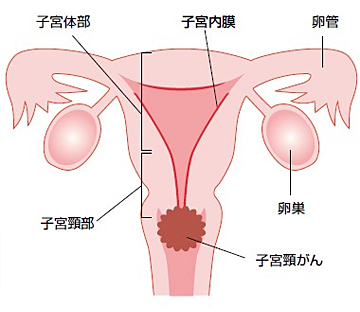
子宮下部に生じる20〜30歳代の若い女性にも多い癌です。当院では手術、放射線療法、化学療法を適切に組み合わせて治療を行っています。
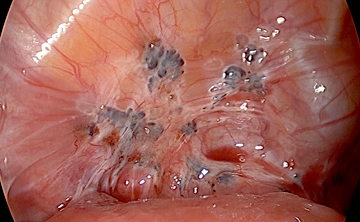
子宮頸癌とは
症状
子宮頸部異形成や初期の子宮頸癌は全く症状がありません。細胞診という検査で子宮頸部の異常な細胞を検出することができますので、無症状のときから婦人科の診察や集団検診などで早めに発見することが可能です。また、月経中でないときや性行為の際に出血したり、普段と違うおりものが増えたりといった症状があるときは、ためらわずに受診することが早期発見につながります。
検査・診断
がん検診においては通常細胞診を行います。子宮頸部の細胞を採取して顕微鏡で観察する検査で、検査に伴う痛みは通常それほど強いものではありません。
細胞診で異常が認められた場合、コルポスコピーという拡大鏡で子宮頸部の粘膜表面を観察する検査を行い、その上で癌が疑われる部分から小さな組織を切り取る組織診を行います。この検査では痛みを感じたり出血したりする場合があります。通常の組織診では評価が不十分な場合、子宮頸部円錐切除術による組織診を行うこともあります(別項参照)。
組織診で子宮頸癌と診断された場合、その広がりをみる検査として、内診、超音波検査、CT検査、MRI検査を行います。場合によって膀胱鏡検査や直腸鏡検査を追加することもあります。
治療
子宮頸癌の治療には大きく分けて手術、放射線治療、抗がん剤による化学療法があります。癌の進行の程度や患者さんの年齢、合併症の有無などからそれぞれの病状に応じて治療方針を選択します。
比較的初期の癌で完全切除が可能な場合は原則として手術を行います。手術の術式は病変の大きさによって決定されますが、病変が小さい場合から順に子宮頸部円錐切除術、単純子宮全摘術、準広汎子宮全摘術、広汎子宮全摘術などの術式が挙げられます。後者ほどより大きな病変に対しても十分な治療成績が得られますが、手術時間がより長く、排尿障害や腸閉塞などの術後合併症の頻度もより高くなります。当院では、癌の治療に支障をきたさない範囲で神経温存手術を取り入れて、排尿障害がなるべく生じないようにしています。また子宮全摘術を行う場合、当院では状況に応じて腹腔鏡手術(詳細は「悪性腫瘍に対する腹腔鏡手術」の項でもご説明しております)も選択可能ですので、主治医にご相談ください。
放射線治療には体の外から照射を行う外部照射と、腟を通して子宮頸部に照射する腔内照射があります。放射線治療は手術を行えない場合に癌の制御を目的として行う場合と、手術後の補助療法として行う場合があります。子宮頸癌に対しては、化学療法を併用する同時化学放射線療法が放射線治療単独よりも有効性が高いことが知られており、当院でも放射線治療科および化学療法部と連携して治療を行っています。
子宮頸癌に対する化学療法は、主に遠隔転移のある症例や再発症例において行われます。当院では主に外来化学療法部において化学療法を行っており、患者さんが自宅での日常生活を安心して過ごせるよう、抗がん剤の副作用による苦痛を軽減する様々な方法をとっています。
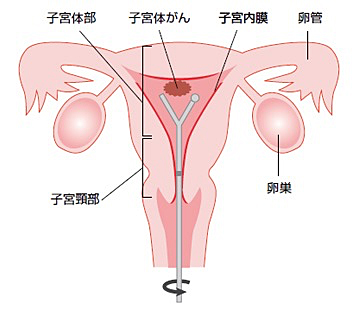
子宮の癌は、子宮頸癌と子宮体癌に分けられます。子宮体癌は子宮体部の内側である子宮内膜から発生する癌です。
症状
月経とは異なる少量の性器出血が続くような場合は、早めに婦人科へご相談ください。
「子宮がん検診を受けているから大丈夫」という方も、子宮がん検診は子宮頸癌の検査を指すことがありますので、注意が必要です。
その他の症状として、下腹部痛や排尿時痛、排尿困難、性行時痛などがあります。
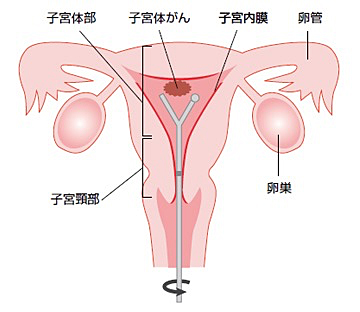
検査
子宮体癌が疑われる方には、内診や経腟超音波検査に加え、子宮内部から細胞を採取して確認する子宮内膜細胞診を行います。
子宮内膜細胞診で癌の疑いがあると判断された場合は、子宮内部を内視鏡で観察する子宮鏡検査や、子宮内膜から生検を行う子宮内膜組織診を行います。
子宮内膜組織診の結果で癌と診断された場合、MRI検査やCT検査で病変の広がり(進行期)を予測します。
治療
癌の治療には一般的に①手術、②抗がん剤、③放射線治療、がありますが、癌の種類により治療法が異なります。
子宮体癌の最も一般的な治療法は手術です。
手術内容は進行期により異なりますが、子宮と両方の卵巣の摘出を行います。リンパ節郭清や大網切除を追加で行うこともあります。
手術は基本的に開腹手術ですが、当院では病変があまり広がっていない、いわゆる早期の癌の場合には侵襲の少ない腹腔鏡手術を行っています(詳細は「悪性腫瘍に対する腹腔鏡手術」の項でご説明しております)。
手術により病変を摘出するとともに正確な進行期を決定し、術後の追加治療を検討します。追加治療には抗がん剤治療などがあります。
術前の検査で手術が困難なほどに病変が広がっていると予測された場合には、手術をせずに抗がん剤治療を行うこともあります。
また、若年の方で妊娠を強く希望される場合には、進行期が早い場合に限りホルモン治療を行うこともあります。
いずれの治療法を選択しても、治療後は再発していないかを定期的に検査していくことになります。
卵巣癌は幼児から老年まで幅広い年齢層で発生する癌です。症状が出るのが遅く、発見されたときにはすでに進行しているケースが多い癌です。
卵巣癌とは
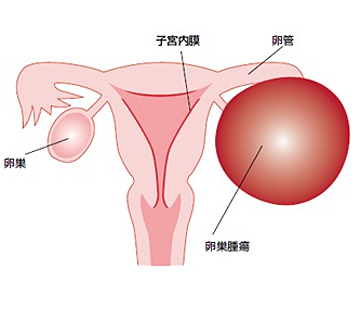
卵巣癌は、かなり大きくなるまで無症状のことが多く、自覚症状に乏しいと言われています。そのため半数以上が診断時に進行がんの状態で発見される事が多いです。腫瘍が大きくなってくると出現してくる症状としては、下腹部の腫瘤感や圧迫感、膀胱が圧迫されて頻尿症状などがあります。お腹のなかに腹水が溜まって腹部全体に膨満感を自覚し食欲が落ちたり、胸に水が溜まって息切れがするといった症状が出て初めて異常に気づく事も少なくありません。
検査
問診、内診(婦人科診察)・直腸診、超音波断層検査、血液検査(腫瘍マーカー)、画像検査(CT検査・MRI検査・PET検査など)を行います。
診断
卵巣腫瘍の治療は、手術が基本になります。良性腫瘍か悪性腫瘍か手術を行って診断し、その後の治療方針を決定します。
治療
卵巣癌の治療には、手術療法、化学療法、放射線療法があります。基本的には、手術で診断・進行期を決定し、その進行期の結果で化学療法を組み合わせていくか検討していきます。進行期によっては化学療法から治療を開始する場合もあります。
手術療法
癌の進行期、年齢、合併症の有無など患者さんの状態に応じて選択します。
- 卵巣・子宮の摘出
- 大網切除
- 後腹膜リンパ節郭清(骨盤内リンパ節、傍大動脈リンパ節)
- 癌が転移している場合、切除可能であれば完全切除を目指します。
完全に切除できない場合は、できるだけ多くの癌を摘出する腫瘍減少手術を行います。
薬物療法-化学療法
卵巣癌は比較的抗癌剤が良く効く癌の一つであり、複数の抗癌剤を併用します。抗癌剤は癌細胞だけでなく正常な細胞にも影響を及ぼすため、その副作用が問題となります。副作用は人によって程度の差があるため、抗癌剤の効果と副作用をみながら行っていきます。
放射線療法
放射線治療は、高エネルギーのX線を患部に照射し、癌を小さくする効果があります。卵巣癌に対して使用するというより、現在は脳や骨などへの転移の症状を緩和するために用いる事があります。
良性疾患(卵巣嚢腫、子宮筋腫、子宮腺筋症)や初期の悪性腫瘍に対し腹腔鏡手術を積極的に行っています。
当院では多くの良性疾患に対し腹腔鏡手術を行っています。
まず臍部に5mm程度の切開を加え、トロッカーという筒を同部位より穿刺し、腹腔内に到達します。そして炭酸ガスによる気腹を行い、腹腔内にスペースをつくります。さらに下腹部に2か所から3か所、5mm~1cm程度の切開を加え、同様にトロッカーを穿刺し、留置します。筒より鉗子などの器具を挿入し、手術を行います。傷が小さく、手術時の負担が軽いのが長所ですが、癒着(組織がひっついていること)が高度な場合や、予想外の出血が起こった場合には開腹術に術式が変更となることがあります。
巣嚢腫とは
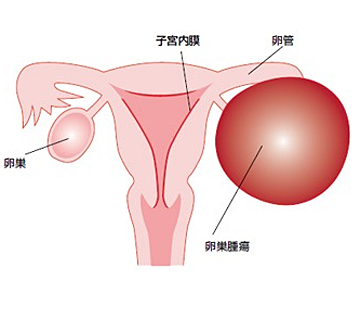
治療
経過観察
嚢腫が見つかってしばらくは、大きくないもの、悪性所見がないものであれば定期的な外来での診察で経過を見ます。卵巣出血や未破裂卵胞は自然消失します。半年たっても縮小ない場合には消失する可能性は低くなります。小さなものであれば定期的な外来受診で様子を見ていきますが、ある程度の大きさになると破裂や捻転(卵巣がねじれること)の可能性が出てくるため手術をお勧めしています。
手術が必要なとき
6㎝以上の大きさがあったり、徐々に大きくなったり、悪性が疑われる場合には治療(手術)が必要です。また激痛を伴い卵巣茎捻転や破裂が疑われる時には緊急手術を行います。
手術方法
悪性が疑われない場合、多くは腹腔鏡の手術を行います。腫れている卵巣を摘出する方法(卵巣切除術)と、腫れている部分のみを摘出する方法(嚢腫核出術)があり、閉経前であれば核出術で卵巣機能を温存することも可能です。悪性が疑われる場合には開腹での手術となります。良性か悪性かの最終的な診断は病理検査で決まります。
チョコレート嚢腫に関しては、ピルなどによる薬物治療も可能です。
子宮筋腫は子宮にできる良性腫瘍です。治療法は開腹手術・腹腔鏡手術・子宮鏡手術などがあります。
子宮筋腫とは
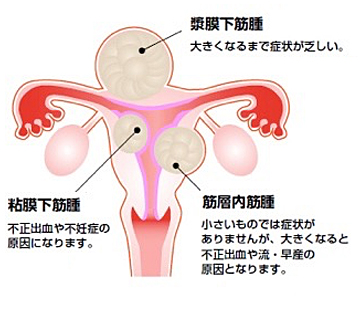
治療
治療としては子宮筋腫によってとくに自覚症状が無ければ経過観察しますが、症状を有し、生活に支障があるようであれば治療が必要となります。治療法には手術と薬物による治療があります。手術では子宮を取ってしまう方法(子宮全摘術)と筋腫だけ取る手術方法(筋腫核出術)があります。将来的にお子様を希望される人では筋腫だけ取る手術を実施しますが、子宮が残っているため再度子宮筋腫が再発してくる可能性があります。
子宮全摘術や筋腫核出術の方法としては開腹手術と腹腔鏡下手術があります。なお粘膜下筋腫であれば子宮鏡下に筋腫を摘出する方法もあります。
薬の治療では閉経状態にしてしまう治療(偽閉経療法)があります。しかし、この治療の間は女性ホルモンの分泌が止められるので骨粗鬆症、更年期障害といった副作用をもたらす可能性があり半年しか治療できません。治療中、月経は止まり子宮筋腫も小さくなることが多いですが、治療を中止するといずれ元の大きさに戻ってしまいます。ですから、筋腫を小さくするために、手術前に一時的に使用するか、閉経に至るまでの一時的治療として行われています。
- 腹腔鏡下子宮体がん根治手術
- 子宮頸がんに対する広汎子宮全摘術
- その他の悪性腫瘍に対する腹腔鏡下手術
腹腔鏡下子宮体がん根治手術
初期の子宮体がんに対して2014年4月より保険適応が認められ、当院では年間に30人以上、これまでに150人以上の患者さんに行っています。
おなかに小さな孔(あな)を数カ所開けて行う腹腔鏡下手術では、開腹による方法と比較して、手術による侵襲を大幅に低減することが可能で、術後疼痛の軽減、入院期間の短縮、早期の社会復帰が可能です。また術中出血量も少なく、腸閉塞などの合併症も少ない傾向にあります。腹腔鏡を用いることにより、骨盤の中の深い部分の観察も直視下に行うより確実に可能であり、出血量の軽減ができます。
子宮体がんの病期の診断は手術後の病理検査で行いますが、手術前と手術中の病理検査にて病期の推測を行い、それぞれの病期に必要な手術を行います。腹腔鏡下子宮体がん根治術の適応となる初期の子宮体がんかどうかは、術前に子宮内膜の組織検査、MRI・CTなどの画像検査で行ない決定します。ただし大きな子宮筋腫や骨盤内に強い癒着がある場合には開腹手術をおすすめする場合があります。また、手術中の病理検査にて、初期の病変でないと診断された場合には腹腔鏡で、もしくは開腹手術に切り替えて、上腹部のリンパ節郭清(傍大動脈リンパ節郭清)を追加して行います。
先進医療:子宮体がんに対する「腹腔鏡下傍大動脈リンパ節郭清術」について
早期の子宮体がんよりも進んだ子宮体がんでは、傍大動脈(みぞおちあたりにある太い血管)の周囲のリンパ節を切除する必要があります。しかしながら、現時点では傍大動脈リンパ節郭清術は腹腔鏡下手術の保険適応ではないため、開腹手術で恥骨からみぞおちまで大きくお腹を切る必要があります。
2017年8月に厚生労働省より先進医療として承認された「腹腔鏡下傍大動脈リンパ節郭清術」では傍大動脈リンパ節郭清術も含めた子宮体がんの手術をすべて腹腔鏡下に行うものです。当院では2018年2月から本術式を導入しています。
「先進医療」では手術費用は全額自己負担となりますが、その他の費用(診察・検査・投薬・入院料等)は、通常の手術と同様に保険診療となります。当院での手術費用は790,420円です。但し予定外の手術の追加が必要となったり、手術中に従来どおりの開腹術に移行した場合、また術後の合併症などに関しては通常どおりの保険診療で行います。
2020年4月から保険適応となりましたので、本術式の先進医療は終了しました。
子宮頸がんに対する広汎子宮全摘術
当院では、早期子宮頸がん(IA2, IB1, IIA1期)に対して、先進医療として2015年6月から行っており、2018年4月から保険診療になりました。
この手術は腹腔鏡を用いて広汎子宮全摘術を行うものです。広汎子宮全摘術とは、子宮と腟の一部に加え、関連するリンパ節も取り除く手術です。
おなかに小さな孔(あな)を数カ所開けて行う腹腔鏡下手術では、開腹による方法と比較して、手術による侵襲を大幅に低減することが可能で、術後疼痛の軽減、入院期間の短縮、早期の社会復帰が可能です。また腹腔鏡を用いることにより、骨盤の中の深い部分の観察も直視下に行うより確実に可能であり、出血量の軽減ができます。
その他の悪性腫瘍に対する腹腔鏡下手術
腹腔鏡下腫瘍生検
CT・MRIなどで骨盤内の悪性腫瘍が疑われるものの、診断がはっきりしない場合には正確な診断を目的として腹腔鏡を用いて骨盤内を検索し、組織の生検を行うことがあります。
開腹手術に比較して、低侵襲で組織を採取し、その後の治療につなげることが出来ます。
月経時に子宮内膜細胞が子宮外で出血するため月経痛や骨盤内癒着、不妊を来すものです。ホルモン治療や外科的手術を行います。
子宮内膜症とは
子宮内膜症とは、本来なら子宮の内腔にある子宮内膜組織が子宮内腔以外の卵巣やお腹の中で発生し、増殖することで月経痛が強くなったりお腹の中で癒着を来したりする病気です。日本では100~200万人の患者がいるといわれています。
症状
月経痛がひどくなって診断される方が多いです。セックスの時に痛かったり、月経時に排便時痛があったりする方もいます。卵巣の子宮内膜症が敗れると、急性腹症となり病院に運ばれることもあります。また、特にそういった症状がないのに、不妊症で見つかる方や、婦人科検診時に卵巣に血液が溜まっていることを指摘されて見つかる方もいます。
検査
内診で子宮周囲の癒着を確認したり、超音波検査で卵巣にふるい血液が溜まっていること(卵巣チョコレート嚢胞といいます)を見つけたりして診断します。血液検査ではCA125という腫瘍マーカーが軽度上昇している方が多いです。卵巣チョコレート嚢胞はとても低い確率で癌化することがあるため、より詳しい検査のために、造影MRIを撮影することがあります。
治療
子宮内膜症は「治る病気」ではなく「付き合う病気」です。命を奪う病気ではないため、子宮内膜症そのものの治療はしなくても、鎮痛剤の工夫や漢方薬などで楽に過ごせるようになる方はたくさんいらっしゃいます。一方、症状が強い場合や不妊症の場合には、子宮内膜症そのものの治療をした方が良いこともあります。今すぐ赤ちゃんを授かりたい、という方には手術療法による癒着剥離術がすすめられますし、(体外受精を計画している場合には専門医との相談が必要です。)卵巣チョコレート嚢胞の癌化が疑われる場合にも手術がすすめられます。そうではない場合、ホルモン療法で治療が可能です。①低用量エストロゲン/プロゲスチン配合薬②ジエノゲスト④GnRHアゴニスト(偽閉経療法)などが主な選択肢になります。それぞれの治療法の特徴をしっかり理解し、自分にあった治療法を医師と一緒に見つけてください。
子宮鏡検査とは
子宮鏡下手術は、子宮鏡で確認しながら子宮内腔の病変を摘出する手術です。摘出した病変は病理検査に提出します。通常は静脈麻酔または脊椎麻酔で行います。
病変の種類や位置などによりますが、 手術時間は30分程度の場合がほとんどです。基本的に日帰りもしくは翌日の退院が可能です。
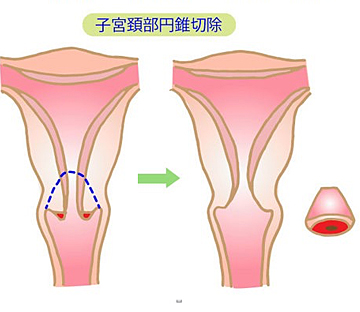
子宮頸部病変 円錐切除術とは
- 外来の検査結果が異型性や上皮内癌までであればすでに浸潤癌になっている部分がないか
- 微小浸潤癌が疑われている場合はさらに進行期の癌ではないか
を確認することが目的です。
病変部を含めて子宮頸部を円錐状に切除し、診断を確定すると同時に、どの程度の治療が必要であるのかを明らかにします。切除をした標本の病理診断の結果が最終診断となります。診断が上皮内癌までであれば追加の治療は通常は不要です。
摘出標本の切り口いっぱいまで病変が達している場合であっても、子宮側の切り口を電気メスで十分に熱凝固するため、十分な治療効果が期待できることが多いですが、より慎重に術後の検診を行ったり、追加の手術を行うことがあります。
円錐切除により多くの方は治癒しますが、細胞の異常をきたした子宮を残した手術になりますので、術後に異型上皮や子宮頸癌が再発する可能性があり、その頻度は3~5%といわれています。手術後も定期的な癌検診は必要です。
方法
腰椎麻酔で行います。
麻酔後、内診の体勢(砕石位)をとり、腟から操作します。
薬剤を塗布して病変部位を確認した後に子宮頸部を電気メスにより止血しながら円錐状に切除します。さらに奥の子宮頸管内の粘膜を採取して検査に提出します。
頸部を円錐状に切除したのち、出血と病巣の取り残しを防ぐという意味で切除した部分に熱変性を加えます。手術時間は30分程度です。
入院スケジュール
原則として、入院期間は原則1泊2日です。
手術当日朝に来院して頂き、術前の準備を行います。
手術当日はご家族に来院していただき、手術中は病院内に待機していただきます。
手術終了後、病棟にうつり、安静のため入院していただき、問題なければ術翌日の午前中に退院となります。
産科

当院では、心疾患、脳血管疾患等の母体合併症を適応とした硬膜外無痛分娩を行っております。産婦人科医・麻酔科医・専門各科医師(循環器内科や脳神経外科等)協力のもと安全に十分留意し計画分娩を行っております。
*2025年7月1日より、母体合併症のない妊婦さんに対しても硬膜外無痛分娩を開始しました。経産婦さんなどを対象に計画分娩を行います。
*当院の無痛分娩を希望する妊婦さんをご紹介いただく際は、紹介状に無痛分娩を希望されている旨を記載のうえ早めにご紹介いただきますようお願いいたします。妊娠週数や予約状況によりご希望にそえない場合もございますので、ご理解・ご協力のほどよろしくお願いいたします。
硬膜外無痛分娩
「無痛分娩関係学会・団体連絡協議会(JALA)」当院登録情報についてはこちら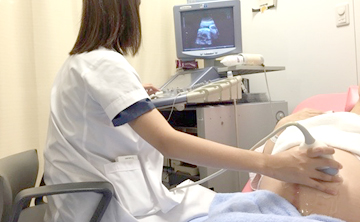

臨床研究
当院産婦人科における臨床研究での患者さんの診療に関する記録の利用について
当院産婦人科科では、子宮頚癌、子宮体癌、卵巣悪性腫瘍、卵巣境界悪性腫瘍の患者さんを対象にした「日本産科婦人科学会婦人科腫瘍委員会 婦人科悪性腫瘍登録事業及び登録情報に基づく研究」を実施しています。
この研究により収集された登録情報を学術的に検討・活用し、産婦人科癌患者の医療・福祉に貢献することを目的としています。平成24年1月1日以降に臨床診断、切除標本や生検により病理診断された子宮頚癌、子宮体癌、卵巣悪性腫瘍、卵巣境界悪性腫瘍の患者さんを対象にデータを収集させていただきます。
この研究は、対象となる患者さんの日常診療で得られる診療に関する記録(検査結果など)を集めますが、特別な治療や検査を行うことはありませんので、患者さんに直接何らかの利益または不利益が生じることはありません。また、対象となった患者さんの住所・氏名など個人が同定されるような情報は、当院以外の第三者に知られることはありません。
ご自身の診療記録がこの研究で利用されることについて異議のある方、または研究内容について詳しく聞きたい方は、担当医もしくは当院の研究責任者にお申し出ください。
当院における連絡先
神戸市立医療センター中央市民病院
研究責任者
産婦人科(部長)
青木 卓哉
〒650-0047 神戸市中央区港島南町2丁目1-1
TEL:078-302-4321、FAX:078-302-2487
研究事務局
(社)日本産科婦人科学会 婦人科腫瘍委員会
臨床研究のお知らせ
| 研究課題名 | 説明文 (PDF) |
| 子宮体がんに対するMSI検査を用いたユニバーサルスクリーニングの成果の検討 | |
|---|---|
| びまん性子宮平滑筋腫症の診断と治療に関する全国実態調査 | |
| DPCデータ及び各レセプトデータ上の妊娠の転帰を特定するvalidation研究 | |
| 卵巣未熟奇形腫の悪性度を判定するバイオマーカーの同定を目指した臨床研究 | |
| JGOG3034 本邦における卵巣成熟奇形腫由来の卵巣がんに対する後方視的調査研究 | |
| 腫瘍HE標本のバーチャルスライドデータ集積及び相同組み替え修復異常と関連する病理組織学的 | |
| 子宮頸癌におけるリンパ節転移がもつ臨床的意義についての検討:多機関共同研究 | |
| 婦人科悪性腫瘍におけるがん遺伝子パネル検査の現状に関する多機関共同観察研究 | |
| DPCデータ及び各レセプトデータ上の妊娠の転帰を特定するvalidation研究 | |
| 日本における卵子提供による妊娠と周産期予後に関する研究―診療録を用いた全国調査研究 | |
| 婦人科悪性腫瘍におけるがんパネル検査の役割:実臨床における運用実態の解明 | |
| 当科における早期前期破水症例の後方視的検討 | |
| 「分娩後動脈性子宮出血」の疾患概念確立のための実態調査 | |
| 婦人科悪性腫瘍におけるがんパネル検査の役割:実臨床における運用実態の解明 | |
| 再発卵巣癌患者の長期寛解生存に関する多施設後方視的検討 | |
| 本邦における子宮体癌に対する低侵襲手術(MIS)の実態調査 | |
| 一般社団法人National Clinical Database(NCD)における手術・治療情報データベース事業 | |
| 妊娠に伴う合併症の早期診断に役立つバイオマーカーと新規治療法の探索 | |
| 本邦における月経異常診断の実態調査 | |
| 成熟嚢胞性奇形腫における腹腔鏡下卵巣嚢腫摘出術の術中破綻が与える影響 | |
| 子宮筋腫と子宮肉腫を術前に鑑別するアルゴリズム作成のための研究 | |
| 高齢子宮内膜癌患者に対する低侵襲手術療法の予後に関する多施設共同観察研究 | |
| プラチナ感受性初回再発卵巣癌に対するオラパリブ維持療法の安全性と有効性を検討するヒストリカルコホート研究 | |
| 日本における新型コロナウイルス感染妊婦の実態把握のための多施設共同レジストリ研究 | |
| 高血圧合併妊娠における妊娠初期の血圧管理が母児に及ぼす影響の検討 | |
| 日本産科婦人科学会婦人科腫瘍委員会 婦人科悪性腫瘍登録事業及び登録情報に基づく研究 | |
| 産科DICをきたした分娩後異常出血症例に対する子宮動脈塞栓術の有用性について | |
| 高血圧合併妊娠における妊娠初期の血圧管理が母児に及ぼす影響 | |
| 日本産科婦人科学会婦人科腫瘍委員会:日本産科婦人科学会婦人科腫瘍登録施設の広汎子宮全摘出術の実態調査 | |
| 胞状奇胎除去術に対する手動真空吸引法(MVA)の安全性や予後についての検討 | |
| AI・機械学習を用いた母子健康状態を至適化する全周産期管理システムの開発 | |
| AI・機械学習を用いた婦人科悪性腫瘍疾患の予後予測システムの開発 | |
| 日本産科婦人科学会周産期委員会 周産期登録事業および登録情報に基づく研究 | |
| 日本産科婦人科内視鏡学会における手術および合併症登録 | |
| 当科における再発婦人科悪性腫瘍に対する腹腔鏡手術の後方視的検討 | |
| 日本産科婦人科学会婦人科腫瘍委員会:本邦における卵巣癌(上皮性腫瘍)に対する妊孕性温存治療に関する実態調査 | |
| IB2-IIB 期の子宮頸部通常型腺癌における術前化学療法の有効性についての後方視的検討 | |
| 「ベバシズマブ10mg/kg/2 週間間隔投与」に対する使用実績調査 | |
| 子宮頸癌における治療前画像(CT、MRI、PET)を用いた根治的同時化学放射線療法(CCRT)における予防的拡大照射の適応に関する検討 |
お知らせ
当院でご出産をお考えの方はこちら一般項目
女性外来受診方法
女性外来受診方法についてはこちら産婦人科外来受診方法
産婦人科外来は可能ならば地元の医師の紹介を頂いて下さい。紹介がありますと、紹介元の先生からの連絡で初診の外来予約がとれます。
予約なしの外来初診も可能です。
| 外来受診案内(初診・予約外) | |
|---|---|
| 外来受付時間 | 月〜金曜日/8:30〜11:00 ※紹介状持参の場合に限り11:30まで受付可能です。 |
メールでの初診予約
申し訳ありませんが、患者様からのメール・電話での外来初診予約は受け付けておりません。
紹介元の先生に所定の手続きを取って頂けましたらFAXでの初診予約が可能です。
紹介元の先生に当院代表電話078-302-4321にお電話して頂いてください。
ご予約がない場合でも外来受診は可能です。紹介状をお持ちになり診察希望日の外来受付時間8:30〜11:30に直接当院外来受付においで下さい。
他院からの紹介状
当院外来は紹介状が無くても受診できますが
紹介状がありますと、
- 他院での医療情報がわかりやすい
- 初診の外来予約がとれる
- 検査の重複が避けられる
- 非紹介患者初診料(7,000円)が不要になる
※当院の他の診療科へ通院していても初診時加算をいただく場合があります。
などの利点がありますので、なるべく紹介を受けて御受診下さい。
どうしても紹介を受けづらい場合は、紹介状なしでも結構です。
紹介状が必要か
当院外来は紹介状が無くても受診できますが
紹介状がありますと、
- 他院での医療情報がわかりやすい
- 初診の外来予約がとれる
- 検査の重複が避けられる
- 非紹介患者初診料(7,000円)が不要になる
※当院の他の診療科へ通院していても初診時加算をいただく場合があります。
などの利点がありますので、なるべく紹介を受けて御受診下さい。
どうしても紹介を受けづらい場合は、紹介状なしでも結構です。
産科
里帰り分娩の受診
妊娠中の異常がなく、予定帝王切開などでもない場合でしたら妊娠34週くらいから当院での妊婦健診を受けてください。
里帰りの時には、現在妊婦健診をしていただいてる先生からの紹介状をご持参ください。
また、里帰り前の妊娠中に、一度当院を受診していただき、入院案内をうけ分娩予約をしていただくことをおすすめします。
帝王切開里帰り分娩の受診
当院で、帝王切開が必要なお産の分娩予約はなるべく32週までに受診して下さい。
受診時には、現在妊婦健診をしていただいてる先生からの紹介状をご持参ください。
他院からの分娩予約
分娩予約は随時お受けしております。
月曜~金曜の産科外来を受診してください。
外来受付時間は8:30~11:30です。
また、これまで妊婦健診を受けられた医療機関から紹介状を発行してもらってください。
紹介状がありますと
- 初診の外来予約がとれる
- 非紹介患者初診料(7,000円)が不要になります
※当院の他の診療科へ通院していても初診時加算をいただく場合があります。
予約手続きについては、紹介元の医療機関か当院代表までお問い合わせください。
帝王切開が必要な里帰り分娩の予約
当院で、帝王切開が必要なお産の分娩予約は、手術予定日を決める都合上遅くても妊娠32週までに受診して下さい。受診時には、現在妊婦健診をしていただいてる先生からの紹介状をご持参ください。
分娩費用について
ご出産された日時(昼間・夜間・平日・休日など)、分娩の内容(特別な処置・薬が必要であったかなど)、赤ちゃんの状態(小児科の処置が必要であったかなど)、入院日数(通常出産後5-6日間)などにより変わりますが、退院時にお支払い頂く費用はおおよそ48万円~58万円くらいです。(神戸市在中の方の場合)
無痛分娩の追加費用は15万円です。(通常の分娩費用に別途加算となります)
帝王切開時の分娩費用
帝王切開時の分娩費用は、入院期間などによりますが40-50万円前後です。
お産の入院で個室は利用できますか
当院産科の個室は陣痛室と重症患者用の治療用個室です。
数に限りがあり、重症患者が優先となります。
空きがあるときに御希望があれば利用可能です。(入院予約の手続きの時に個室希望をおたずねします)
申し訳ございませんが、正常分娩の産後は総室(4人部屋)になります。
婦人科
癌検診
当神戸市の医療機関の役割分担により、当院では紹介患者・救急患者さんを中心に診療をしております。
一般的な1次癌検診(まだ がん になっていない方対象の予防的検診)につきましては、原則、地元の病院・開業医さんを紹介しております。
更年期障害
更年期障害につきましては、カウンセリング・薬物療法を中心とした継続的な治療が必要です。
また神戸市の医療機関の役割分担により、当院では紹介患者・救急患者さんを中心に診療をしております。そのため当院では原則、地元の病院・開業医さんを紹介しております。
令和7年度採用産婦人科専攻医募集
当科での産婦人科研修について
当科を基幹施設とする産婦人科研修プログラムでは、毎年、若干名の産婦人科専攻医(後期研修医)を公募しております。
全国から意欲的な先生が集まり、3年間の実践的な研修を受け、立派な産婦人科医として巣立っています。
本年も産婦人科専攻医を若干名募集いたします。
当院の後期研修の理念
周産期領域、婦人科領域、生殖医療、さらに産婦人科救急疾患の基本的、かつuptodateな診療を実践的に学ぶ。`腕の立つ`産婦人科専門医としてこれからの日本の産婦人科医療をリードできる人材を育成する。
目標
(1)腫瘍・婦人科
良性疾患では、単純子宮全摘除術などの開腹手術が執刀でき、卵巣腫瘍などの腹腔鏡下手術ができるようになる。悪性疾患では、悪性腫瘍手術を含めた総合的管理、化学療法、放射線療法、悪性疾患患者との接し方を体得し、広汎子宮全摘出術・傍大動脈郭清などの前立ちができるようになる。
(2)周産期
正常分娩および代表的な異常分娩が取り扱えるようになる。とくに母体、胎児の切迫した危険性が、遅滞なく把握でき、対応できるようになる。急速遂娩、とくに吸引分娩、緊急帝王切開の判断と実行ができるようになる。また産科的多量出血、産科的DICに対応できるようになる。
(3)生殖医学
タイミング療法、排卵誘発法、人工授精など外来で行う一般的な不妊治療を身につける。子宮内膜症に対しては積極的に腹腔鏡による診断・治療をおこなう。体外受精などの高度生殖医療の研修も可能。
(4)産婦人科救急
産婦人科救急疾患に単独で初期対応できるようになる。とくに緊急手術などの迅速な判断と執刀が出来るようになる。
施設認定
総合周産期母子医療センター、地域がん拠点病院、日本婦人科腫瘍学会専門医修練施設、日本周産期・新生児学会暫定研修基幹施設、日本産婦人科学会専門医制度卒後研修指導施設(専攻医終了の段階で、日本産婦人科学会認定専門医および母体保護法指定医師の申請資格可能)産婦人科研修プログラム基幹病院
診療実績(令和元年)
| 手術総計 | 1,379件 |
|---|---|
| 婦人科手術 | 1,056件 |
| うち悪性腫瘍 | 247件 |
| 腹腔鏡 | 471件 |
| 分娩数 | 821件(うち帝王切開302件) |
週間予定
| 毎朝 | ミーティング(当直医報告・前日手術ビデオレビュー・症例検討) ※新病院のIT機能を生かして、密度の濃いミーティング・カンファレンスを毎日行っています。 |
|---|---|
| 月曜日 | 画像カンファレンス・放射線治療カンファレンス(放射線診断部・治療部合同) |
| 火曜日 | 産科回診・周産期カンファレンス(NICU合同)・スポンサードレクチャー |
| 水曜日 | 婦人科回診・術前カンファレンス |
| 木曜日 | ジャーナルクラブ・症例レクチャー・腫瘍カンファレンス(病理部・腫瘍内科合同) |
| 金曜日 | 術前カンファレンス |
| 手術日 | 月~金曜日 |
| 後期研修医外来担当 | 約週1日 |
| 当直 |
約週1〜2回(当直あけは原則duty free) |
各部門の特徴
腫瘍・婦人科部門
神戸市の中心的癌治療施設であり、日本婦人科腫瘍学会専門医修練施設として日本婦人科腫瘍学会専門医・日本がん治療認定医の指導のもと、高度な癌手術・集学的治療を研修できる。また関西屈指の腹腔鏡手術実施施設であり、産婦人科内視鏡学会認定指導医・技術審査委員のもとで腹腔鏡・子宮鏡手術を多症例研修できる。関連科として外科・泌尿器科での短期研修も可能である。
周産期部門
兵庫県の総合周産期センターであり、様々な合併症妊娠・異常分娩が学べる。関連科としてNICU研修が可能である。
生殖医療部門
腹腔鏡による子宮内膜症治療・子宮鏡下手術などを多数例研修できる。神戸市内の生殖医療実施施設にて顕微受精・卵管鏡・生殖遺伝カウンセリングなどの院外専門研修を受けることができる。
婦人科救急
神戸市全域より1~3次救急を24時間受け入れているため、3年間でほとんどの産婦人科救急疾患の治療が体得できる。
学会活動
学会・研究会・セミナーなどへの積極的な参加・学会発表を行っている。後期研修期間に全国的学会発表・筆頭論文作成をおこなう。
大学病院との連携
京大病院の関連施設として、「京大病院マグネット病院連携を基盤とした専門医養成プログラム」に参加しており、京大病院産婦人科および関連病院での研修も可能。また、関西医科大学の臨床教育病院でもある。
後期研修終了後の進路
当科または、関連病院の産婦人科スタッフとして推薦・紹介する。大学に進学し大学院生や研究生として研究したり、留学したりすることも可能である。後期研修終了時に各自に希望の病院があれば、推薦する。若い産婦人科医は全国的に非常に不足しており、特に当科からのスタッフを希望する病院・入局を歓迎する大学病院が多数ある。
成27年度〜後期研修,男性医師
みなさんは産婦人科後期研修に何を求めるでしょうか。人それぞれに求めるものは違いますが、自分が重視し、実際に体験して感じた当院での研修の長所をご紹介したいと思います。
圧倒的な症例数:当院では年間1300件程度の手術があり、1年目から約150件以上の手術を執刀することができます。特に腹腔鏡手術については、後期研修可能な日本の病院の中でも最も多く経験を積める施設の一つといえるでしょう。また、件数が多いだけではなく術後に先輩や医長クラスの先生からフィードバックをもらえることもいいところです。
各分野のプロフェッショナルがいる:当院には各専門分野のプロフェッショナルが揃っており、また気のいい方々ばかりなので、気軽に相談することができ、あらゆる症例について専門家の意見をもらうことができます。不妊については実際の治療を行っていませんが、元々専門分野としていたスタッフがおります。
オン・オフがしっかりしている:仕事が忙しいだけでは人生を楽しく過ごすことはできません。当院は当直医制であり、基本的に分娩や救急症例はその日当直の先生が対応します。当直にあたらない休日は休息や趣味に当てる先生も多く、皆人生を謳歌しています。また、他科の専攻医との交流も多く、金・土・日は飲みに行くこともしばしば。神戸には美味しいお店も多いですよ。
色々書きましたが、とにかく一度見学しにきてください!
平成29年6月
平成26年度〜28年度 後期研修,女性医師
初期研修から連続して、今年の3月に後期研修を修了することができました。非常に充実した研修だったと感じています。
当院の産婦人科研修では、産科・婦人科ともに幅広く学ぶことができ、手術も多く経験できます。また、救急疾患への対応力についても鍛練が可能な環境です。
また、希望があれば他施設への研修も可能であり、自主性が尊重されています。医局全体の雰囲気は和気あいあいとしており、コメディカルも協力的な方ばかりなので、のびのびと研修ができると思います。
新しい仲間が増えるのを楽しみにしています。是非研修にお越しください。
平成29年6月
平成25年度〜27年度 後期研修,女性医師
他院で初期研修を行った後、後期研修から当院で勤務をしています。
後期研修の病院を決定するにあたり私が重視したのは、周産期から婦人科まで幅広く学べることと、手術を含め数多くの症例を経験できることの2点でした。産婦人科専門医取得までの3年間ですべての領域をバランスよく学ぶことは産婦人科医としての礎を築く上で重要です。ただ周産期から腫瘍、女性医学まで多岐に渡る産婦人科領域をバランスよく十分に研修できる病院というのはなかなかないのではないかと思います。
当院は総合周産期センターで症例が多く、通常の妊婦健診からハイリスク症例の妊娠管理までを学ぶことが出来ます。婦人科分野についても、悪性疾患の診断から手術加療、また外来での管理まで一貫して学ぶことが可能です。もちろん一般的な婦人科疾患の管理も十分に学べます。それに加え3次医療機関として救急症例も多いため、産科・婦人科に関わらず様々な救急疾患を経験できます。日々忙しく大変なこともありますが産婦人科を学びたい方には当院での研修は充実感の溢れたものになるはずです。スタッフの良さも当院の売りです。ぜひ当院で一緒に研修をしましょう!やる気にあふれた皆さんをお待ちしています。
平成29年6月
平成21年度〜23年度 後期研修,女性医師
後期研修医二年目です。神戸市の基幹病院として、多岐にわたる診療を行っている病院の中で日々研修させてもらっています。一番の特徴は周辺地域から多くの合併症妊婦、婦人科疾患の患者さまが集まり、時には24時間当直中の各科の専門医の先生方の協力も得ながら1次から3次までの疾患の診療にあたっていることです。緊急手術も多く、帝王切開だけでなく緊急処置の必要な婦人科の患者さんの診療も学ぶことができます。そして平日の毎日が手術日となっていて腹腔鏡の手術から開腹手術、腟式、子宮鏡手術などの様々な手術を執刀医や助手として経験できます。これらの診療は初期研修医終了時の3年目の春の時点では、もちろんまったく不可能でしたが、指導医に朝から晩まで、外来・手術・当直と指導してもらうことで徐々に身につけてこれていると思っています。指導医の先生だけでなく、研修医の先輩の先生方にすぐに相談できる環境があるので、初めての事ばかりでも安心して診療にあたることができます。自分の担当患者さんとして症例を一つ一つ経験すると同時に、研修医仲間の症例からもいろいろな知識・技術を吸収していくことができるよう、ミーティングやカンファレンスが常時おこなわれている事も当科の良い点です。女性の一生を支える医療ができるように日々精進しています。是非一緒に研修しましょう。
平成22年9月
癌治療
現在の癌治療は、担当科を中心に、病院各科全体による集学的治療が必要です。当院は、神戸市癌診療の地域拠点病院および近畿圏屈指の高度総合医療施設として、また、日本の婦人科癌診療において中心的役割を担ってきた京都大学医学部婦人科学産科学教室の代表的関連施設として、神戸市内はもとより兵庫県・近畿各県より癌患者さんを受け入れています。指導医は日本婦人科腫瘍学会認定専門医・指導医です。
関連リンク
(以下作成予定)
- 子宮体癌治療
- 卵巣癌治療
- 悪性腫瘍に対する腹腔鏡手術
- 広汎子宮全摘術における神経温存手術
- リンパ節郭清時のリンパ浮腫低減手術
- 放射線療法・化学療法同時併用治療
- 在宅療養(中心静脈栄養・緩和医療など)
- 腹腔内抗癌剤治療
- 子宮内膜増殖症ホルモン治療
緩和治療
癌の診療において、抗癌治療(手術・放射線・抗癌剤)にならんで大切な治療が緩和治療です。これは、痛み・発熱・嘔気・不眠・不安など癌による諸症状を緩和することを目的とした医療で、抗癌治療と平行して行われます。最近では疼痛緩和・制吐・抗不安のための薬剤の腫瘤も増え、症状に合わせた色々な処方・投薬が可能になっています。
当院では緩和ケア外来と全科的な緩和医療チームがあり、緩和医療に効果を上げています。
腹腔鏡手術
最近の手術技術と器材の進歩により、多くの手術が腹腔鏡で行うことが可能になりました。従来の開腹術に比べ術後疼痛・癒着などが少なく、早期退院が可能です。傷も目立たずにすみます。当科では産婦人科としての年間実施件数は近畿有数です。指導医は日本産科婦人科内視鏡学会技術認定医です。
実施可能な腹腔鏡下手術は次のようなものです。
- 子宮体癌手術
- 子宮頸癌手術(先進医療実施準備中)
- 子宮全摘出術
- 子宮筋腫核出術
- 卵巣嚢腫摘出術
- 卵巣・卵管摘出術
- 子宮内膜症手術
- 不妊症検査
- 子宮外妊娠術
- 避妊手術
- 子宮脱手術
- その他
子宮鏡手術
最近の手術技術と器材の進歩により、子宮鏡でいろいろな手術が可能になりました。従来の開腹術に比べ術後疼痛などが極めて少なく、早期退院が可能です。傷も残りません。実施可能な子宮鏡下手術は次のようなものです。
- 筋腫核出術
- 内膜焼却術
- 内膜ポリープ切除術
- 双角子宮手術(中隔切除)
- その他
子宮筋腫
子宮筋腫は子宮に発生する良性腫瘍で、子宮に発生する腫瘍の内では、最も頻度の高いものです。治療を必要としない小さなものまで含めると、35才以上の婦人の、約20%に筋腫を認めるといわれています。治療の段階としては次の段階があります。
1.特に治療の必要がなく、定期的な検診で経過観察できる場合
- 子宮癌の検診で異常がない。
- 月経困難症(生理痛)・月経過多・腰痛・貧血など現在筋腫によると思われる症状が許容範囲である(鎮痛剤・造血剤程度で管理可能)。
- 大きさが手拳大以下で、以前に比べて筋腫の大きさ・症状に増悪がない。
この場合半年に一回の定期検査が必要です。月経がある間は筋腫は少しずつ大きくなります。しかし閉経すれば筋腫は次第に縮小します
2.薬で治療する必要がある場合
- 上記症状が日常生活に支障がある。
- 以前に比べて筋腫の大きさ・症状に増悪をみとめる。
ホルモン剤により月経を止める方法が一般的です。薬での治療中は病状は軽減し筋腫は縮小しますが筋腫を消すことはできません。効果には個人差があり、治療を中止すると再発します。一時的に筋腫を抑えておく(閉経または手術まで)のが主な目的です。
3.手術が必要な場合
- 薬の治療では効果が十分でない。
- 薬の副作用が強い。(更年期症状・骨密度の低下など)
- 癌検診で異常がある。
- 子宮筋腫が不妊症の原因と考えられる。
子宮筋腫の根本的な治療には手術が必要です。
4.手術の方法
筋腫核出術(腹腔鏡、開腹、子宮鏡)
筋腫のみをくり抜きます。子宮は残るが将来筋腫が再発する可能性が残ります。術後に妊娠を希望する場合など子宮を残したい場合におこないます。腹腔鏡下に行える場合と開腹が必要な場合があります。子宮腔内の筋腫(粘膜下)は子宮鏡下での手術が可能です。
膣式子宮摘出術
お腹を切らずに膣から子宮をとります。筋腫が大きい・膣が狭い・癒着がある場合などは困難です。
腹腔鏡下子宮摘出術
膣式摘出が困難場合に内視鏡(腹腔鏡)を併用しながら膣から子宮を取ります。従来、筋腫が大きすぎたり癒着がひどいために開腹が必要であった場合でも開腹なしで手術が行える最新の方法です。
腹式子宮摘出術
お腹を切って子宮をとります。非常に大きい筋腫・癒着がひどい場合・悪性の疑いがある場合などに行います。
卵巣嚢腫
卵巣に水や粘液などがたまり、大きく腫れたものを卵巣嚢(のう)腫といいます。腹部膨満・痛みなどを自覚することがありますが、自覚症状のないまま偶然発見されることも多いです。良性の場合と悪性(卵巣癌)の場合があります。また、子宮内膜の組織が子宮内腔以外の場所へ発生する子宮内膜症という病気が原因で、卵巣に内出血が起こり腫れる場合(古い出血が溶けたチョコレートのようになるため卵巣チョコレート嚢腫と呼ばれます)、排卵時に卵巣に内出血が起きて血が溜まるもの(卵巣血腫)・排卵(卵巣から卵子がはじけ出ること)がきちんと起きずにそのまま嚢胞として残ってしまっているもの(未破裂卵胞)なども卵巣嚢腫として診断されることがあります。
自然に様子を見た場合どうなるか
大きくないもの(直径4-6cm以下)や悪性所見がないもので、診断後間もない場合は、しばらく定期検査で経過観察します。卵巣血腫や未破裂卵胞は自然消失する可能性が高いです。3ヶ月~半年以上持続する卵巣嚢腫は、自然消失する可能性は低く、治療しない場合は継続的な定期検診が必要です。無症状・無変化のままで経過することも少なくありませんが、大きな嚢腫はときに嚢腫の破裂・茎捻転などがおこり腹痛の原因になることがあります(この場合は緊急手術になります)。また、長期観察中に悪性変化(癌の発生)がみられることがあります。
治療が必要な場合
悪性の疑いがあったり、直径4~6cm以上と大きい場合や、徐々に大きくなったりする場合は治療(手術)が必要です。です。また、激痛を伴う茎捻転や破裂は、緊急手術になります。長期にわたって消失しない卵巣嚢腫は無症状・無変化でも将来の癌化の危険性を考慮して、適当な時期に手術することも必要でしょう。
どのような手術が必要か
悪性の疑いがない場合は≫腹腔鏡の手術で行います(腹腔鏡下卵巣嚢腫摘出術または卵巣摘出術)。閉経前の場合は、卵巣の健常部分を残す手術も可能です。手術の所要時間は1時間~2時間です。入院は数日です。悪性の疑いがある場合などは、開腹手術が必要になります。卵巣嚢腫の最終診断(悪性・良性の区別を含めて)には術後の病理検査が必要です。
卵巣腫瘍に必要な検査
一般健診としては、内診・超音波診断(膣式または腹式)、精密検査としてはMRI撮影・CT撮影・腫瘍マーカー(血液検査)などが必要です。
子宮内膜症
子宮内膜症とは、子宮の内側にある内膜組織が何らかの原因で、本来あるべき所以外の場所で発育、増殖する病気です。
子宮内膜は卵巣からのホルモンに反応して増殖し、月経の時にははがれて出血が起こります。同様に子宮内膜症も月経の時には内出血をおこし、周囲の組織と反応して痛みの原因となります。これが月経のたびにくり返されるため周りとの癒着がおこります、卵巣では内出血がチョコレート状に溜まった嚢腫となります(チョコレート嚢腫)。子宮内膜症の主な発生部位は子宮の壁(子宮腺筋症)、子宮と直腸の間(ダグラス窩)、仙骨子宮靱帯(子宮の付け根)、卵巣などです。
症状
子宮内膜症の代表的な症状は、月ごとにひどくなっていく月経痛です。また、月経の時以外でも腰痛・下腹部痛・性交痛・排便痛などがみられる場合があります。不妊症の原因にもなります。一方、自覚症状がほとんどない場合もあります。
治療法
子宮内膜症の治療には、薬物療法・手術療法あるいはその併用療法があり、患者さんの年齢や症状に応じて使い分けられます。
1.薬物療法
軽症の場合は消炎鎮痛剤による生理痛の管理と定期検診で様子を見ます。症状の強い場合はピルで排卵のない弱い月経にしたり偽閉経療法でホルモン剤により月経を止める治療を行います。子宮内膜症の増殖や出血が止まり、病巣部は萎縮し、しだいに痛みなどの症状が改善します。治療期間は3~6ヶ月です。偽閉経療法の副作用として一過性ですが更年期様症状がみられることがあります。長期治療を繰り返すと骨密度の低下をきたす場合があります。
2.手術療法
病巣の摘出・焼却、癒着剥離などを行います。妊孕性の温存や再発のリスクの軽減のためには腹腔鏡による丁寧かつ徹底的な手術が必要です。当科ではレーザーや超音波メスなどを駆使し効果を上げています。子宮内膜症では入院期間は約1週間で、全身麻酔が必要です。
子宮腺筋症
産婦人科子宮線筋症子宮腺筋症とは子宮の壁(子宮筋層)にできた子宮内膜症です。
子宮筋腫のように子宮が腫大し、月経の度に子宮内に内出血が起こるため、ひどい生理痛と卵巣や腸との癒着がおこります、卵巣そのほかの子宮内膜症を合併することも多いです。
症状
子宮線筋症の代表的な症状は、月ごとにひどくなっていく月経痛です。また、月経の時以外でも腰痛・下腹部痛・性交痛・排便痛などがみられる場合があります。不妊症の原因にもなります。
治療法
子宮腺筋症・子宮内膜症の治療には、薬物療法・手術療法あるいはその併用療法があり、患者さんの年齢や症状に応じて使い分けられます。
1.薬物療法
軽症の場合は消炎鎮痛剤による生理痛の管理と定期検診で様子を見ます。すぐに妊娠を望まない場合にはピルを服用すると生理痛が緩和され腺筋症および内膜症が軽快します。症状が強い場合は偽閉経療法といって、ホルモン剤により月経を止める治療を行います。子宮内膜症の増殖や出血が止まり、病巣部は萎縮し、しだいに痛みなどの症状が改善します。方法は1日2回の点鼻薬または月1回の注射です。治療期間は3~6ヶ月です。副作用として一過性ですが更年期様症状がみられることがあります。長期治療を繰り返すと骨密度の低下をきたす場合があります。ダナゾール(ボンゾール)の局所療法が有効である場合もあります。
2.手術療法
根本的な治療法は子宮の摘出です。一定の条件下で子宮を温存した子宮腺筋症の摘出術も可能です。合併する子宮内膜症に対しては病巣の摘出・焼却、癒着剥離などを行います。妊孕性の温存や再発のリスクの軽減のためには丁寧かつ徹底的な手術が必要です。当科では腹腔鏡によるレーザーや超音波メスなどを駆使し効果を上げています。
担当看護師制
当院に初めて入院されるときに担当看護師が付きます。治療が長期にわたるときに、継続的な看護や細かいご相談に応じることが可能です。
女性外来
性発育・月経・更年期・老年期・性病・性交渉などの女性特有の体の不調について、女性医師による相談室を設けています。完全予約制ですので、病院外来事務 (病院代表電話 078-302-4321)までお問い合わせ下さい。
詳しくはこちら合併症妊娠・分娩
神戸市の基幹総合病院としてまた救急病院として、各科の協力の下、病気を持ちながらの妊娠出産、一般病院では管理困難な未熟児が予想される早産や、妊娠高血圧症候群・子宮内胎児発育不全などの妊娠中の合併症をもつ妊婦さんを積極的に受け入れています。
合併症(ハイリスク)妊娠・分娩では、出産後の児の管理も重要です。当院は神戸市および兵庫県南部の周産期センターとして多くの母体搬送・新生児搬送を受け入れています。小児科・新生児科が管理する未熟児・新生児センターは産科病棟に隣接し、産科との全面的な協力の下、当院で生まれたすべての児を含む新生児の管理を行っています。
未熟児・新生児センター(NICU)
胎児超音波外来
現在の妊婦健診において、超音波診断は必要不可欠なものとなっております。これにより、分娩予定日の修正や、詳しい赤ちゃんの発育について診断可能になってきています。また、最近の産科超音波診断技術の進歩により、分娩前に様々な胎児疾患も診断されるようになってきております。特に胎児疾患の診断には特別な技術とある程度の検査時間が必要です。
すでに、当科ではすべての妊婦さんに超音波検査を受けて頂いておりますが、一般の妊婦健診の時間内では胎児疾患などの十分な検査への対応ができにくくなってきております。そのため当科では、超音波診断に最も適している妊娠中期頃(妊娠20週~30週)により専門的な超音波胎児診断を受けて頂くための特殊外来を設けております。
赤ちゃんの病気を妊娠中にチェックする事で、分娩前に新生児センター・小児科と連携をとり、妊娠、分娩、出生後の赤ちゃんの管理に役立てることが可能です。超音波検査だけで赤ちゃんの病気がすべて見つかる訳ではありませんが、ぜひ受けていただくようにお勧めいたします。
料金は2,000円です(当院初診の場合は別に初診料7,000円が必要です)
(なお、患者様のご希望によるビデオ録画は、現在おこなっておりません。あしからずご了承下さい。)
当院の妊婦健診に来られていない方でも受診可能です。
かかりつけ医に相談し、地域医療推進課を通じて、FAX予約をして下さい。
NIPT
最近、産婦人科領域でNIPT(非侵襲性出生前遺伝学的検査)という出生前に母体血を用いて特定の胎児染色体異常を調べる検査の認識が広がっており、当院でも実施体制を整え基幹施設の認証を取得し、遺伝カウンセリングおよび検査を行っています。
NIPTは、母体血を調べることで赤ちゃんが染色体疾患(21トリソミー・18トリソミー・13トリソミー)をもつ可能性を検査するものです。NIPTを受けることが選択肢となるのは、これらの染色体疾患の発生頻度が高くなる以下のような場合とされています。
*高年齢の妊婦さん
*母体血清マーカー検査で、赤ちゃんが染色体数的異常を有する可能性が示唆された場合
*染色体数的異常のある赤ちゃんを妊娠した既往がある妊婦さん
*両親のいずれかが均衡型ロバートソン転座を有していて、赤ちゃんが 13 トリソミーまたは 21 トリソミーとなる可能性が示唆される場合
*胎児超音波検査で赤ちゃんが染色体数的異常を有する可能性が示唆された場合
ただし、対象疾患の発生頻度によらず、遺伝カウンセリングを実施しても赤ちゃんの染色体数的異常に対する不安が解消されない妊婦さんについては、十分な情報提供や支援を行った上でご本人の意思決定を尊重させていただきます。
当院では妊娠10~14週で単胎もしくは双胎妊娠の妊婦さんにNIPTを実施しております。羊水検査を行う場合は、妊娠16~18週に行います。
遺伝カウンセリングおよび検査については、周産期遺伝相談外来で行っております。周産期遺伝相談外来の予約やご案内は当院産科外来で行っておりますので、
・当院産科外来へ通院中の方でNIPTを希望される場合は、主治医にご相談ください。
・他院かかりつけで当院でのNIPTを希望される方は、かかりつけの産婦人科医にご相談いただき、当院産科外来の受診予約をお取りください。
まず、よくあるご質問について(FAQ)をご参照ください。追加のお問い合わせは下記メールアドレスへお問い合わせください。
神戸市立医療センター中央市民病院 産婦人科医局 obgyn@kcho.jp(パソコンからのメール着信拒否にしている場合、返信内容が届かないのでお気をつけ下さい)
お急ぎの場合は神戸市立中央市民病院までお電話またはFAXでお願い致します。
神戸市立医療センター中央市民病院
病院代表 電話 078-302-4321 FAX 078-302-7537
なお、ご相談の内容によってはメール・電話・FAXでお答えできない場合もございます。
- 先進医療:子宮体がんに対する「腹腔鏡下傍大動脈リンパ節郭清術」について
2020年4月から保険適応になりましたので、本術式の先進医療は終了しました。詳細は「悪性腫瘍に対する腹腔鏡手術」をご参照ください。